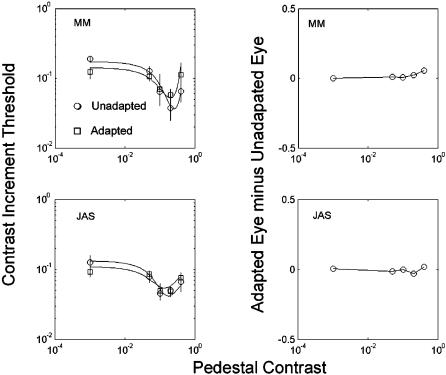
Figure 4.
Results of a dichoptic experiment in which the adapting stimulus was in one eye while the other eye saw a blank field. Thresholds as a function of pedestal contrast were then obtained either in the adapted eye or the non-adapted eye. The left-hand panels show the mean (across eyes) for the adapted and non-adapted conditions. The continuous lines are maximum-likelihood fits to these data using the model described in Methods. The effect of adaptation is similar to that of a lower contrast binocular adapter (Fig. 3, top panel). Note that adaptation improves detection performance (leftmost point) in both observers. The right-hand panel shows the difference in threshold between the adapted and the non-adapted eye, in the adapted condition. There is evidence for slightly greater masking at high pedestal levels in the adapted eye, but not at low and intermediate pedestal contrasts.