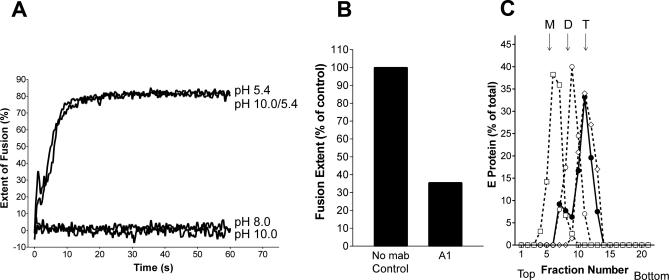
Figure 6. Analysis of Membrane Fusion, E Dissociation, and Trimerization at Different pH Values.
(A) Fusion of pyrene-labeled TBE virus with liposomes was carried out at 37 °C at the following conditions: (i) virus and liposomes were mixed an adjusted to pH 5.4, (ii) virus and liposomes were mixed and kept at pH 8.0, (iii) virus and liposomes were mixed and adjusted to pH 10.0, and (iv) virus and liposomes were preincubated at pH 10.0 for 10 min before adjustment to pH 5.4. The corresponding curves are labeled pH 5.4, pH 8.0, pH 10.0, and pH 10.0/5.4, respectively.
(B) Extent of low pH–induced fusion of pyrene-labeled TBE virus pretreated at pH 10.0 in the absence (control) and the presence of the FP-specific monoclonal antibody A1. The figure shows the values obtained 1 min after acidification.
(C) Sedimentation analysis demonstrating the low pH–induced trimer formation of virions preincubated at pH 10.0. Virions and liposomes were preincubated at pH 10.0 for 10 min, adjusted to pH 5.4 (filled circles), solubilized, and subjected to sucrose density centrifugation as described for Figure 2. As controls (dotted lines), virions were incubated for 10 min at pH 10.0 (boxes), pH 5.4 (diamonds), or pH 8.0 (open circles), solubilized, and analyzed as described above. The sedimentation direction is from left to right, and the positions of E monomer (M), dimer (D), and trimer (T) are indicated.