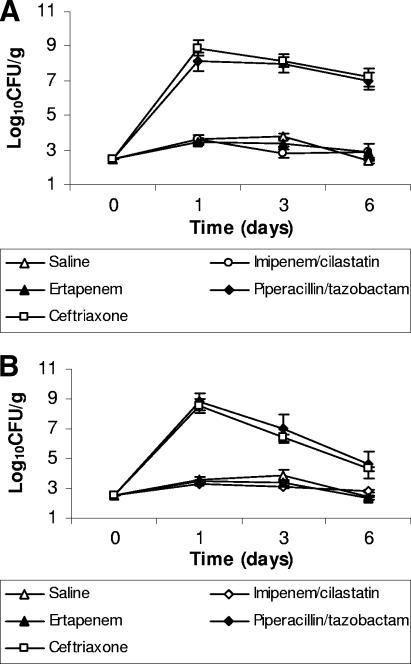
FIG. 2.
Effect of subcutaneous antibiotic treatment on the establishment of colonization with extended-spectrum β-lactamase-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae (A) and vancomycin-resistant enterococci (B) in mice exposed to the pathogens 2 days after completion of antibiotic treatment. Mice received antibiotic treatment once daily for 5 days, and 2 days after completion of antibiotics (day 0), 104 CFU of one of the pathogens was administered by orogastric gavage. If the pathogens were not detected in stool samples, the lower limit of detection (∼2 log10 CFU/g) was assigned.