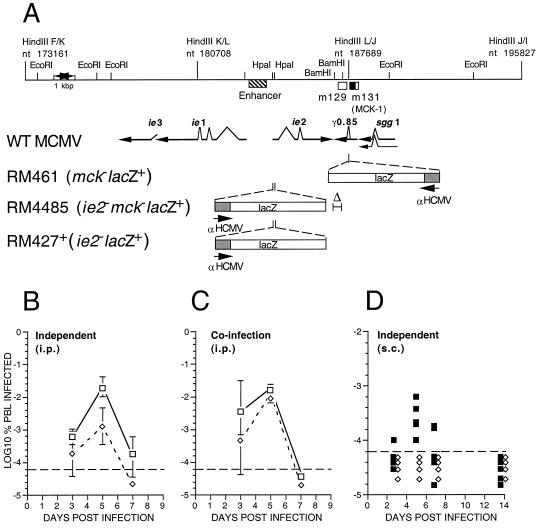
Figure 3.
Murine CMV MCK-1/MCK-2 mutant construction and evaluation of viremia during infection of mice. (A) Map of the HindIII K, L, and J fragments of wild-type murine CMV (WT MCMV; K181+ strain) showing the position of the m129 and m131 ORFs (17), as open boxes, and the predicted MCK-1 ORF within m131 as a filled box. The murine CMV ie1/ie2/ie3 transcriptional enhancer and the arrangement of ie1, ie2, ie3, sgg1, and γ0.85 transcripts also are shown with splicing patterns indicated on the arrows depicting individual transcripts. The lacZ insertion mutations in the three recombinant viruses (RM461, RM4485, RM427+) as well as the deletion mutation disrupting γ0.85 transcript expression in RM4485 are depicted below the map. The genome structure and growth properties of RM461, which carries a lacZ insert disrupting the γ0.85 transcript expression, has been described (12, 29). Expression of the lacZ gene in all recombinant viruses was regulated by a 199-bp human CMV ie1/ie2 promoter (αHCMV) fragment (−219 to −19 relative to the transcription start site) (22). This promoter fragment exhibits immediate early expression kinetics when adjacent to the murine CMV transcriptional enhancer, as in RM427+ and RM4485, and delayed early expression kinetics in RM461 (12). (B) Levels of viremia after infection with K181+ (□) or RM4485 (⋄). BALB/c mice 3 or 4 weeks of age were inoculated by the i.p. route with 1 × 106 plaque-forming units of virus, and PBLs were harvested by heart puncture at 3, 5, and 7 days postinfection. Infection rates were expressed as the percentage of total PBLs that scored positive in an infectious centers assay on monolayers of NIH 3T3 cells. Error bars represent standard deviation of the means of titers in five mice. (C) Levels of viremia after co-infection with K181+ and RM4485. Mice were co-inoculated by the i.p. route with a 1:1 mixture of K181+ and RM4485 at 1 × 106 plaque-forming units, and PBLs were harvested as described in B. Infectious centers were stained to reveal β-galactosidase expression and to differentiate RM4485 from K181+ plaques. (D) Levels of viremia after s.c. inoculation of RM427+ (■) or RM4485 (⋄) inoculated into one or two hind footpads were analyzed as above, except the results of individual mice were plotted as separate points. The dashed line in each panel represents the limit of detection.