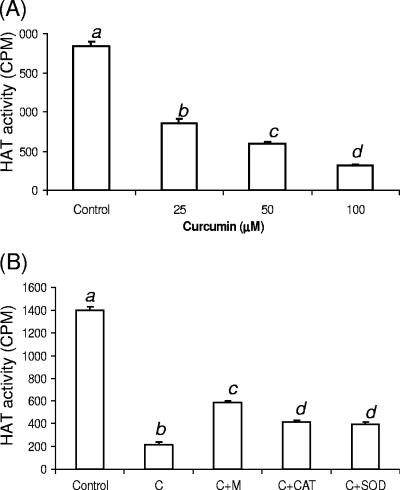
FIG. 4.
Effects of curcumin on in vivo HAT activity in P. falciparum. (A) Dosage-dependent inhibition of HAT activity in vivo. HAT activity in the same amount of nuclear extracts from control and curcumin-treated parasites for 8 h was measured using PfH3. (B) ROS scavenger and antioxidant enzymes antagonized curcumin-induced inhibition of HAT activity. HAT activity was measured with PfH3 and equal amounts of nuclear extracts from untreated (control) parasites and parasites treated with 50 μM curcumin alone (C) or coincubated with 300 μM mannitol (M), 5,000 units/ml catalase (CAT), or 400 units/ml superoxide dismutase (SOD). Values in each graph labeled with different letters are significantly different (Tukey's HSD test, P < 0.001). The means plus standard deviations (error bars) from three replicate samples are shown.