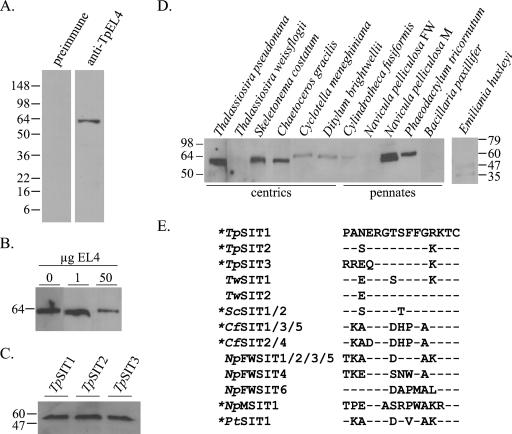
FIG. 2.
Characterization of anti-TpEL4. Molecular mass markers (kDa) are shown on the left or right side of each immunoblot derived from SDS-PAGE separations. (A) Immunoblot of T. pseudonana whole-cell protein lysates using preimmune serum and anti-TpEL4 indicated that the antibody specifically recognized a protein with a size consistent with the predicted size of SITs. (B) Immunoblot of protein lysates probed with anti-TpEL4 preincubated with 0, 1, or 50 μg of TpEL4 peptide demonstrated the specificity of the antibody for the epitope against which it was raised. (C) Immunoblot of Saccharomyces cerevisiae transformed to express TpSIT1, TpSIT2, or TpSIT3 demonstrated that the antibody recognized each of the three T. pseudonana SITs. (D) Immunoblot of 10 μg of total protein lysate from various centric and pennate diatom species and the coccolithophore Emiliania huxleyi. (E) Amino acid alignment of SITs from different diatoms in the region used to generate anti-TpEL4. The sequence of TpSIT1 is shown on the first line. SIT sequences are identified by the initials for genus and species as follows: Tp, Thalassiosira pseudonana; Tw, Thalassiosira weissflogii; Sc, Skeletonema costatum; Cf, Cylindrotheca fusiformis; NpFW, Navicula pelliculosa FW; NpM, Navicula pelliculosa M; and Pt, Phaeodactylum tricornutum. Dashes indicate residues identical to those of TpSIT1. Asterisks indicate proteins from species that cross-reacted with anti-TpEL4.