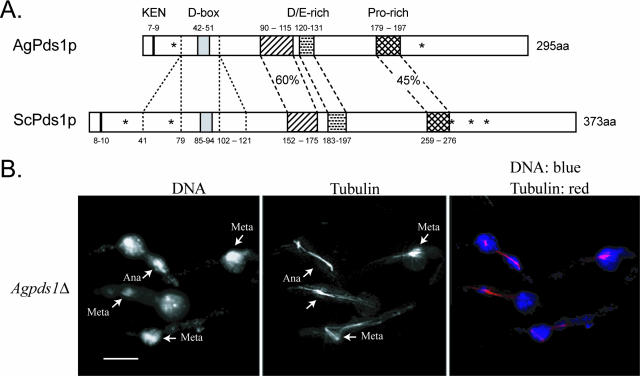
FIG. 4.
(A) Comparison between AgPds1p (AGR083W) and ScPds1p (YDR113C). The percent identity between the two proteins is 29%. N-terminal protein destruction motifs (KEN box and D box) are noted in addition to three conserved regions in the middle of Pds1p, one highly enriched in negatively charged amino acids (aa) and one enriched for proline, all of which are conserved in yeast species. A major difference between Pds1p orthologues of Saccharomyces species and A. gossypii is the absence of 39 amino acids upstream and 20 amino acids downstream of the D box. Pds1 orthologues from K. waltii and K. lactis also lack blocks of amino acids of similar sizes in this region. The asterisks in ScPds1p mark the positions of five CDK consensus phosphorylation sites (T27, S71, S277, S292, and T304); only two (T27 and S292) are conserved in AgPds1p (T23 and S213) and in seven other yeast orthologues. (B) Spores from Agpds1Δ heterokaryons (NSG03) were incubated under selection for 18 h at 30°C and processed for DNA and tubulin staining. Cells arrested as germlings with one germ tube, most of which carried one nucleus, arrested in either metaphase (Meta) or anaphase (Ana) (arrows denote different stage nuclei). Bar, 10 μm.