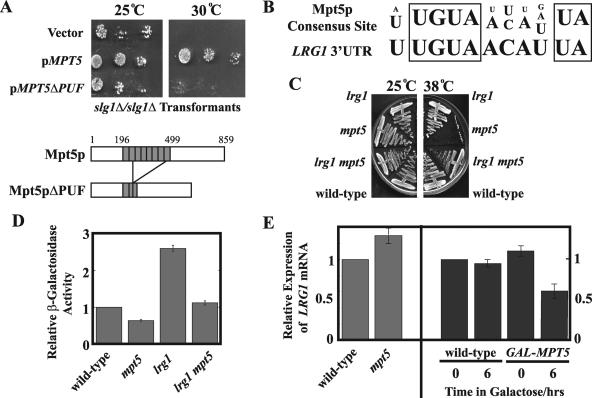
FIG. 5.
Mpt5p destabilizes the LRG1 transcript to regulate CWI signaling. (A) The PUF domain of Mpt5p is required for function in the CWI pathway. slg1Δ/slg1Δ (JVG1081) mutants were transformed with a vector (YEp24), pMPT5 (pYK601), or pMPT5ΔPUF. After selection on the appropriate medium, the transformants were grown in selective liquid medium and diluted to an OD600 of 0.02. This dilution was spotted along with two further 1:100 dilutions onto two selective plates, one grown at 25°C and the other at 30°C. The plates were incubated for 3 days. (B) The Mpt5p consensus binding sequence (6) matches the putative Mpt5p-binding sequence in the LRG1 3′UTR. (C) Loss of LRG1 suppresses mpt5 mutants. Wild-type (JVG161), mpt5Δ (JVG2110), lrg1Δ (JVG2976), and mpt5Δ lrg1Δ (JVG2989) cells were plated on rich medium plates and grown at either 25°C or 38°C for 3 days. (D) Loss of LRG1 suppresses the Pkc1p signaling defect of mpt5 mutants. Wild-type (JVG161), mpt5Δ (JVG2110), lrg1Δ (JVG2976), and mpt5Δ lrg1Δ (JVG2989) cells were transformed by conventional methods with the pRlm1-lacZ reporter construct, which faithfully reports on Slt2p activity in vivo. Reporter activity was quantified for each transformant grown to mid-logarithmic phase in synthetic medium at a permissive temperature. (E) Mpt5p regulates the LRG1 mRNA level. Wild-type (JVG161) and mpt5Δ (JVG2110) cells were cultured to mid-logarithmic phase in YPD medium at room temperature and collected, and total RNA was prepared. A GAL-MPT5 strain (TTC75) and its congenic wild type were cultured to mid-logarithmic phase in YP-raffinose and transferred to YP-raffinose or YP-galactose and cultured for 6 h. Samples (t = 0 and t = 6 h) were collected, and total RNA was prepared. All RNA samples were Northern blotted. Transcripts were detected by phosphorimaging. The LRG1 transcript level was quantified relative to the ACT1 transcript control for each sample, and relative expression values between samples were calculated relative to untreated wild-type control samples.