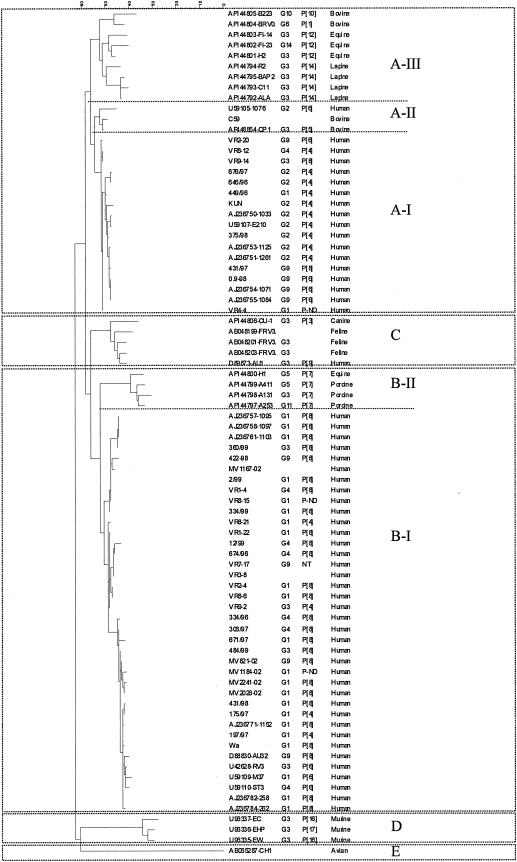
FIG. 2.
Phylogenetic tree of rotavirus NSP4 sequences constructed by the maximum parsimony method. The genotype-defining clusters were confirmed by bootstrap values of >90% (not shown). Sequences available from GenBank/EMBL from human and animal rotavirus strains (accession numbers and strain identifiers are in the first column) were included alongside representative NSP4 nucleotide sequences of human strains from this study for comparison. G and P type (where available) and host of origin are indicated after each strain identifier or accession number.