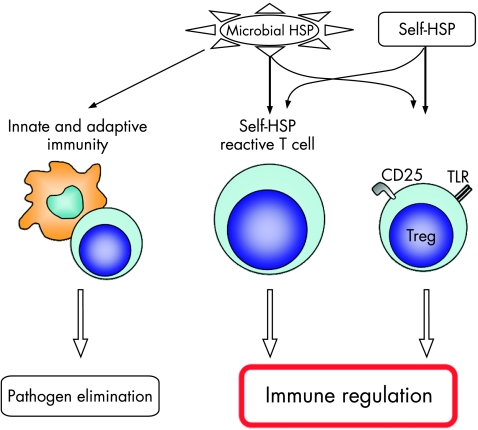
Figure 1 The complexity of heat shock protein (HSP)–immune‐system interactions. Microbial HSPs trigger both innate and adaptive immune reactions leading to pathogen elimination in infection. Self‐HSPs are involved in immune reactions leading to immunoregulation. Conserved epitopes of microbial HSP trigger self‐HSP‐reactive T cells, which lead to immunoregulation. By this, in the kinetics of microbial HSP immunity, proinflammatory responses are followed by inflammation dampening immunoregulation. In addition, self‐HSPs activate through the direct triggering of innate receptors on regulatory T (Treg) cells. TLR, toll‐like receptor.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.