Involvement of the central nervous system is one of the most devastating manifestations of Behçet's disease. We describe a patient with refractory neuro‐Behçet's disease, successfully treated by infliximab, a chimeric monoclonal antibody to tumour necrosis factor α (TNFα).
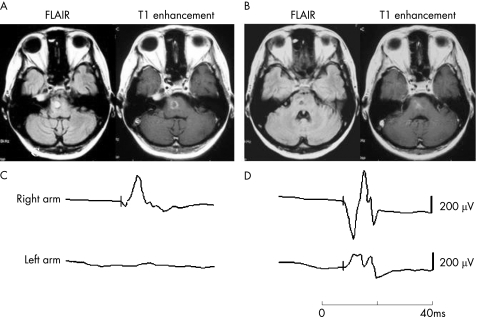
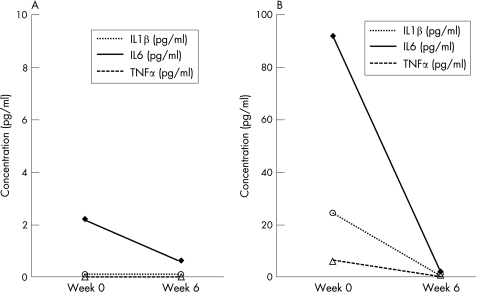
A 36‐year‐old Japanese woman, already diagnosed as having Behçet's disease on the basis of recurrent appearance of orogenital ulcers and bilateral uveitis, was referred to the First Department of Internal Medicine, Graduate School of Biochemical Sciences, Nagashaki University Hospital. On admission, neurological examinations showed cerebellar ataxia and pyramidal tract involvement. Examination of the patient's cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) showed a total cell count of 576/mm3 with 56% neutrophils; protein was 128 mg/dl. A conventional therapeutic regimen, including intravenous methylprednisolone and cyclophosphamide and oral methotrexate, was used; however, she did not respond well, and had sudden‐onset left hemiplegia. Axial magnetic resonance fluid attenuated inversion recovery images showed a high signal intensity lesion in the right pons, and a T1‐weighted image showed ring‐like enhancement. Altough she was given five doses of intravenous methylprednisolone, the abnormal findings on magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) still remained (fig 1A). She was then infused with 3 mg/kg infliximab at weeks 0, 2 and 6 after obtaining her informed consent. MRI performed after the second infliximab infusion showed a reduction in the abnormal signal intensity in the right pons (fig 1B). The left hemiplegia gradually improved, and the patient gained the ability to walk using a cane. Motor evoked potentials (MEPs) in the left arm were not evoked before infliximab treatment (fig 1C); however, a positive MEP wave was obtained after infliximab treatment (fig 1D). Cytokine production, in both serum and CSF, was also examined during the treatment (fig 2). Compared with serum, protein concentrations of TNFα, interleukin (IL)1β and IL6 were high in CSF before infliximab treatment but were markedly reduced after the treatment. Daily oral prednisolone could be reduced from 60 mg to 15 mg.
Figure 1 Axial magnetic resonance fluid attenuated inversion recovery images and T1‐weighted magnetic resonance images (MRI) with gadolinium enhancement before (A) and after (B) infliximab treatment. Abnormal MRI features were clearly retained by conventional treatment (A); however, the area was reduced by infliximab (B). Motor evoked potentials evoked by transcranial magnetic stimulation were absent in the left arm before infliximab treatment (C), but appeared after infliximab treatment (D).
Figure 2 Cytokine profiles in the serum and cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) during infliximab treatment. Protein concentrations of tumour necrosis factor (TNF)α, interleukin (IL)1β and IL6 were high in the CSF (B) compared with levels in the serum (A). Infliximab clearly reduced the concentrations of TNFα, IL1β and IL6 in both the serum and CSF.
Inflammation in Behçet's disease is thought to be mediated by cytokines, especially by TNFα.1 TNFα is believed to be located upstream of cytokine networks,2,3 and thus infliximab may reduce the production of IL1β and IL6. Previous studies indicate that MEPs evoked through transcranial magnetic stimulation are valuable in monitoring the disease activity or therapeutic response of neuro‐Behçet's disease.4 The appearance of an MEP wave may be indicative of the regeneration process after central nervous system damage, and the present case suggests that transcranial magnetic stimulation can be used as an alternative qualification method to monitor motor tract dysfunction. MRI evidence of parenchymal contrast enhancement is assumed to indicate disruption of the blood–brain barrier.5 The breakdown of the blood–brain barrier may permit the access of infliximab to the cerebral parenchyma, resulting in the suppression of TNFα‐mediated inflammatory processes.
Neither long‐term studies nor clinical trials with large numbers of patients have been carried out on the use of infliximab to treat neuro‐Behçet's disease6,7; however, this case, the first report of an Asian patient, strongly suggests that infliximab brings about an immediate and dramatic improvement in refractory neuro‐Behçet's disease, indicating its application in cases of life‐threatening neurological manifestations of Behçet's disease.
Footnotes
Competing interests: None declared.
References
- 1.Misumi M, Hagiwara E, Takeno M, Takeda Y, Inoue Y, Tsuji T.et al Cytokine production profile in patients with Behçet's disease treated with infliximab. Cytokine 200324210–218. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Arend W P. The innate immune system in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 2001442224–2234. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Hermann J, Walmsley M, Brennan F M. Cytokine therapy in rheumatoid arthritis. Springer Semin Immunopathol 199820275–288. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Bent S, Saeed B, Donald R M, Mohammed Z A. Transcranial magnetic stimulation in Behçet's disease: a cross‐sectional and longitudinal study with 44 patients comparing clinical, neuroradiological, somatosensory and brain‐stem auditory evoked potential findings. Clin Neurophysiol 20001111320–1329. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Afshin B H, Rahman P, Ali‐Reza N. neuro‐Behçet's disease. Neurologist 20051180–89.15733330 [Google Scholar]
- 6.Licata G, Pinto A, Tuttolomondo A, Banco A, Ciccia F, Ferrante A.et al Anti‐tumour necrosis factor alpha monoclonal antibody therapy for recalcitrant cerebral vasculitis in a patient with Behçet's syndrome. Ann Rheum Dis 200362280–281. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Sarwar H, McGrath H, Espinoza L R. Successful treatment of long‐standing neuro‐Behçet's disease with infliximab. J Rheumatol 200532181–183. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]