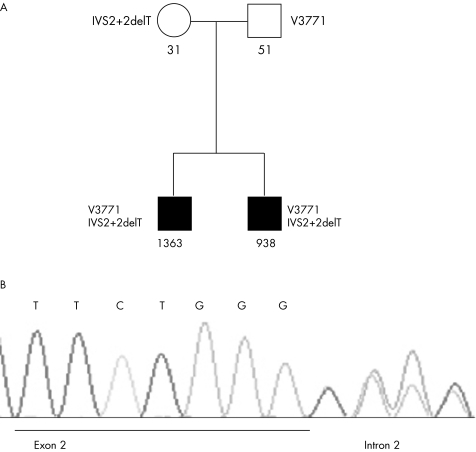
Figure 1 (A) depicts the family tree of hyperimmunoglobulinaemia D syndrome. Females are indicated by circles and males by squares. Solid symbols denote affected members. The mevalonate kinase (MVK) mutations are listed on the left and right sides of the members. Note that the parents are heterozygotic for MVK mutations whereas both siblings are compound heterozygotic for V377I and IVS2+2 delT. The IgD serum concentrations are listed below the members. The serum concentrations of the affected siblings are grossly increased (normal <100 IU/ml), whereas those of the nonaffected father and mother are normal. (B) shows the electrospherogram with sequence identification of the deletion of a T nucleotide in intron 2. This mutation, IVS2+2 delT, is predicted to affect correct splicing of the exon, resulting in a shift of the reading frame.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.