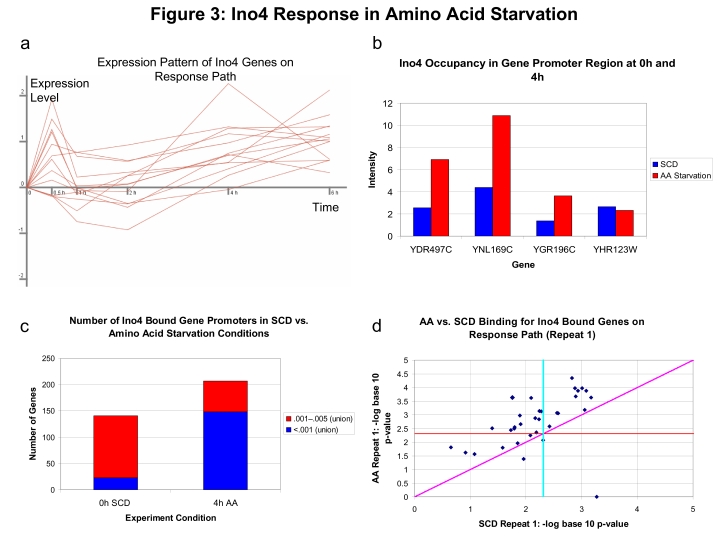
Figure 3.
The role of Ino4 in regulating response to AA starvation. (A) Expression profiles of 13 genes in AA starvation that were assigned to the brown path in Figure 2B. These 13 genes were all bound by Ino4 in a ChIP-chip experiment in YPD media with a P-value <0.005 and have an evolutionarily conserved Ino4 motif. It was predicted by DREM that Ino4 was activating these and other genes starting around 2 h (see also Supplementary Table 4). (B) Occupancy rates of Ino4 in the promoter region of four genes regulated by Ino4, before and at 4 h after AA starvation. For three of these four genes, the Ino4 promoter occupancy rates were at least two-fold higher following AA starvation than in synthetic complete+D-glucose (SCD) media before AA starvation. (C) Comparison of the number of genes bound by Ino4 before and 4 h after AA starvation using a whole-genome binding experiment. We compared the lists using two different P-value cutoffs (0.001 and 0.005). Genes were counted if they are bound at the appropriate P-value in at least one of the two repeats. At the 0.001 P-value cutoff, there is almost a six-fold enrichment for Ino4-bound genes 4 h after AA starvation. (D) Comparison of binding P-values for genes assigned to the main path determined by DREM to be regulated by Ino4 in one of the repeats (see also Supplementary Figure 2). The plots are the negative log base 10 of the binding P-value for genes that were bound with a P-value <0.005 in one or more of the Ino4 binding experiments and are on the identified Ino4 response path. The horizontal and vertical lines represent a P-value significance of 0.005. Anything to the right of the vertical line is significant under normal growth conditions. Anything above the horizontal line is significant in the AA starvation experiment. Anything above the diagonal line is more significant in the AA starvation experiment. This plot indicates that these genes were bound more significantly in AA starvation conditions than SCD conditions.