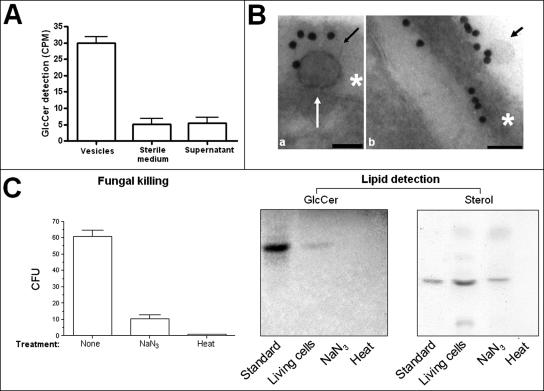
FIG. 3.
Vesicle production requires cell viability. (A) The addition of radioactive ceramide precursors to the culture medium results in the detection of significant levels of radioactive GlcCer in vesicle preparations. In 100,000 × g pellets from sterile medium and in 100,000 × g supernatants of grown cells, significant levels of radioactive GlcCer were not detected (P < 0.001). (B) GlcCer-containing vesicles are apparently transferred from the plasma membrane to the cell wall (a) and then secreted (b). Scale bars represent 100 nm. Arrows point to vesicles, and asterisks are on the cryptococcal cell wall. (C) Killing of cryptococci with sodium azide or heating demonstrates a decrease in cell viability of 83% (sodium azide) and 99% (heat), as determined by comparison with CFU counts obtained with untreated yeasts. Lipid analysis of 100,000 × g fractions of the supernatants obtained after fungal killing revealed the detection of GlcCer in fractions from living but not heat- or azide-treated cells. Compounds with migration rates corresponding to an ergosterol standard were detected in 100,000 × g fractions from supernatants of living and azide-treated cells but not in preparations from heat-killed cryptococci. CPM, counts per minute.