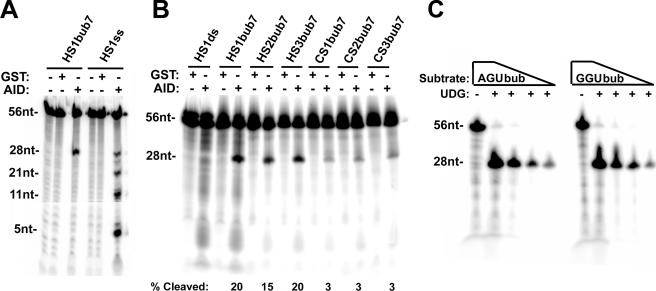
FIG. 2.
Deamination analysis on hot- and cold-spot bubbles. (A) Deamination assay showing GST-AID activity on a bubble substrate (HS1bub7) as well as the single-stranded HS1ss (the radioactively labeled strand of HS1bub7). As indicated at top, GST was purified in parallel with GST-AID and used as a control for the specific activity of AID. The top band represents the 56-nucleotide labeled strand and the lower band represents the 28-nucleotide product of deamination due to alkaline cleavage at the target C in the bubble. UDG was added to all reactions. (B) Deamination assay comparing AID activities on three hot-spot bubbles (HS1bub7, HS2bub7, and HS3bub7) and three cold-spot bubbles (CS1bub7, CS2bub7, and CS3bub7). HS1ds was used as a control for the single-stranded DNA activity of AID. The band intensities were quantitated, and the amount of cleaved product resulting from deamination as a percentage of the entire labeled DNA in each lane is shown below each substrate. (C) As a control to ensure that the UDG step of the activity reaction does not discriminate between WRU and non-WRU motifs, UDG (without AID) was incubated with serial dilutions of AGUbub or GGUbub substrates which were designed to be analogous to HS1bub7 and CS3bub7 but with the target cytidine on the labeled strand replaced by uridine. nt, nucleotide.