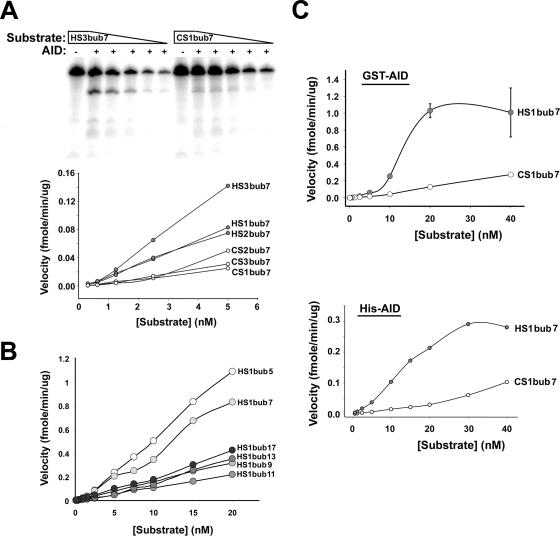
FIG. 3.
Deamination kinetics on hot- and cold-spot bubbles. (A) Representative deamination assay showing the activity of GST-AID on serial dilutions of a hot-spot and a cold-spot bubble. Assays were performed on the indicated hot-spot bubbles and cold-spot bubbles using constant concentrations of GST (−) or GST-AID (+) and twofold serial dilutions of the substrate starting with 5 nM. The product and substrate bands were quantitated and used together with the incubation time and the amount of AID to calculate the reaction velocity at each substrate concentration (graph). Velocity is defined as the amount of deaminated product generated by a given amount of AID in a unit of time and plotted against substrate concentration. (B) Deamination kinetics showing the activity of GST-AID on dilutions (starting with 20 nM) of hot-spot substrates with the same WRC motif (AGC) located within different bubble sizes ranging from 5 (HS1bub5) to 17 (HS1bub17) nucleotides. (C) Reaction velocity plotted against substrate concentration carried out over a 1,000-fold range of substrate concentration (starting with 40 nM) on HS1bub7 and CS1bub7 for GST-AID and His-AID.