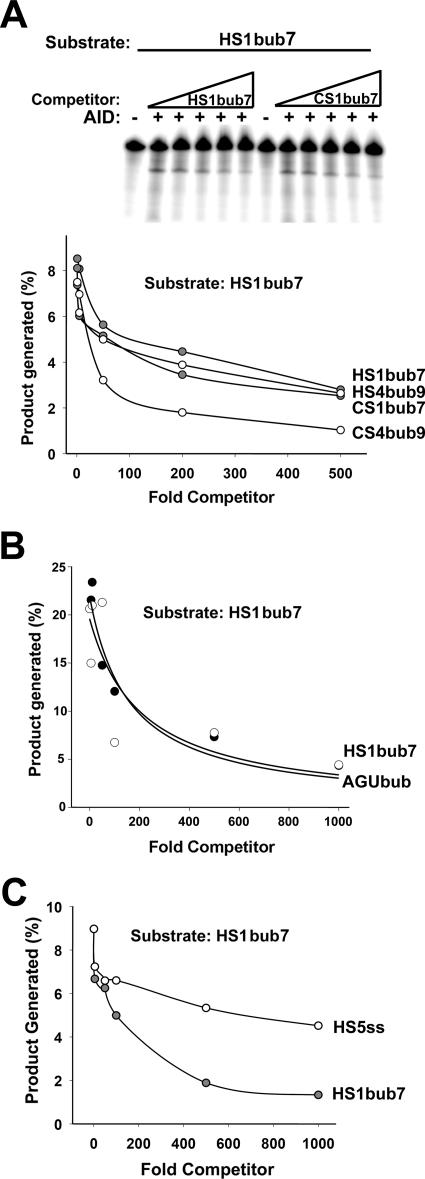
FIG. 6.
Deamination inhibition by hot- and cold-spot competitors. (A) Upper panel shows a representative deamination assay using GST (−) or GST-AID (+) with 50 fmol of HS1bub7 as substrate. Reactions were carried out in the presence of increasing amounts (5- to 500-fold) of excess unlabeled hot-spot bubble competitor (HS1bub7) or cold-spot bubble competitor (CS1bub7) which were added to the reaction mixture before the addition of AID. Additional deamination inhibition assays were performed using HS1bub7 as the substrate and excess unlabeled HS1bub7, HS4bub9, CS1bub7, and CS4bub9 as cold competitors (gels not shown), and the results are shown in the graph. For each lane, the amount of cleavage product was quantitated and expressed as a percentage of total substrate. This value is shown on the y axis as a function of the increasing amounts of unlabeled competitor on the x axis. (B) Graphs are as described for panel A, except that 20 fmol of HS1bub7 was used as the substrate and unlabeled HS1bub7 and AGUbub were used as excess unlabeled competitors (5- to 1,000-fold excess). (C) Graphs are as described for panel A, except that HS1bub7 and HS5ss were used as excess unlabeled competitors (5- to 1,000-fold excess).