FIG. 1.
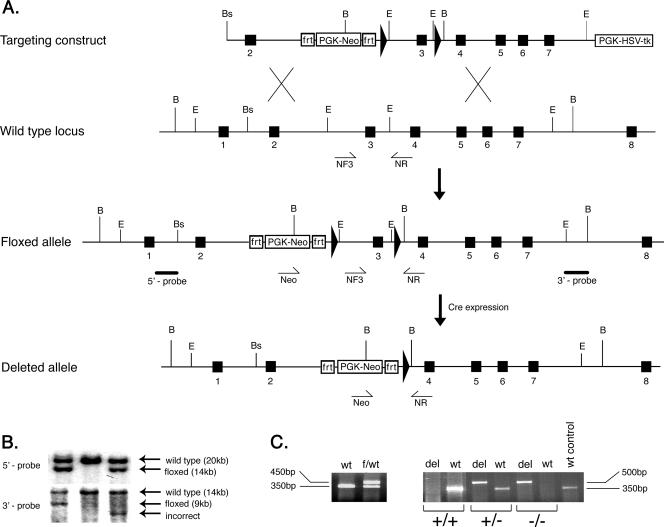
Generation of the myotilin-deleted allele (myo−/−). A. The top diagram shows the targeting vector constructed by subcloning genomic myotilin fragments into the pDELBOY-3X vector. The exons are depicted by filled boxes, and the loxP sites are shown as filled arrows. Relevant restriction site positions are marked by letters as follows: B, BamHI; E, EcoRI; Bs, BssI. The second diagram shows partial genomic organization of the wild-type murine myotilin gene. NF3 and NR represents the relative positions of the genotyping primers used to detect the wild-type allele. The third diagram shows the organization of the conditional (floxed) allele after homologous recombination in ES cells. The solid bars below the intronic regions represent the 5′ and 3′ probes used for detection of correct recombination. The bottom diagram shows the final organization of conditionally deleted myotilin gene, missing exon 3. The deletion was obtained in vivo by crossing the mouse bearing the flox allele with a Cre-expressing mouse. The Neo and NR primers used for genotyping and detection of the deleted allele are shown schematically as arrows under the genomic locus. PGK-HSV-tk, herpes simplex virus type I thymidine kinase under the phosphoglycerine kinase promoter cassette; PGK-Neo, neomycin gene under the phosphoglycerine kinase promoter. The PKG-Neo cassette is flanked by two frt sites. B. Southern blot of BamHI-digested genomic DNA from three ES clones. The upper panel represents the autoradiography after hybridization with the 5′ probe, shown in panel A. The expected recombination events are observed in the left and right lane, where the wild-type allele of 20 kb and the floxed allele of 14 kb are indicated by arrows. The middle lane shows the control wild-type alleles. In the lower panel, detection of the recombination was done using the 3′ probe. The left lane shows correct recombination events by detection of the wild-type allele of 14 kb and the floxed allele of 9 kb. The middle lane shows only the wild-type allele, and the right lane depicts incorrect recombination events. C. The left panel shows a 350-bp fragment from the wild type (wt) and 450 bp from the floxed allele (f) generated in one PCR with primers NF3 and NR. The right panel shows the genotype of the mice after in vivo Cre-mediated recombination. Wild-type (+) and deleted (−) alleles were detected using two PCRs for each sample. Primers Neo and NR generate a 350-bp fragment from the wild type and 500 bp from the deleted allele (del). The right lane shows a wild-type (+) control reaction.