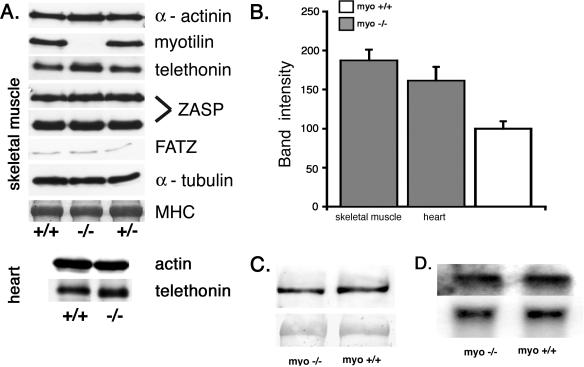
FIG. 3.
Immunoblot and Northern blot analysis of muscle proteins. A. The presence of Z-disk proteins was investigated by immunoblotting using crude skeletal and cardiac muscle homogenates of myo+/+, myo−/−, and myo+/− mice. The immunoblot with antimyotilin antibody 151 shows lack of reactivity in the myo−/− muscle, indicating the absence of the protein. α-Actinin, ZASP (32-kDa and 78-kDa isoforms), FATZ-1, and α-tubulin are normally expressed. Instead, a markedly increased telethonin reactivity is observed in the skeletal muscle and a minor increase is detected in the cardiac muscle. Myosin heavy chain (MHC) detection using Coomassie staining of the postblotted gel served as a loading control. B. Quantification of telethonin content in skeletal and cardiac muscle of myo−/− mice. Western blot intensity of the telethonin signal (n = 3) was normalized to the actin content detected with the monoclonal AC40 antibody. The data obtained from nine measurements are reported as means + SEM of the telethonin content in the myo+/+ skeletal or cardiac muscles, which was assigned 100 (SEM = 14.26). C. Western blot analysis of an ∼200-kDa muscle palladin isoform in skeletal muscles. The upper panel shows equal amounts of palladin detected with E1a antibody. The lower panel shows Ponceau S-stained nitrocellulose membrane to illustrate an equal amount of protein loading. D. Northern blot analysis of myopalladin transcript in the skeletal muscle. The upper panel is the myopalladin probe, and the lower panel is a β-actin probe used as a loading control.