Abstract
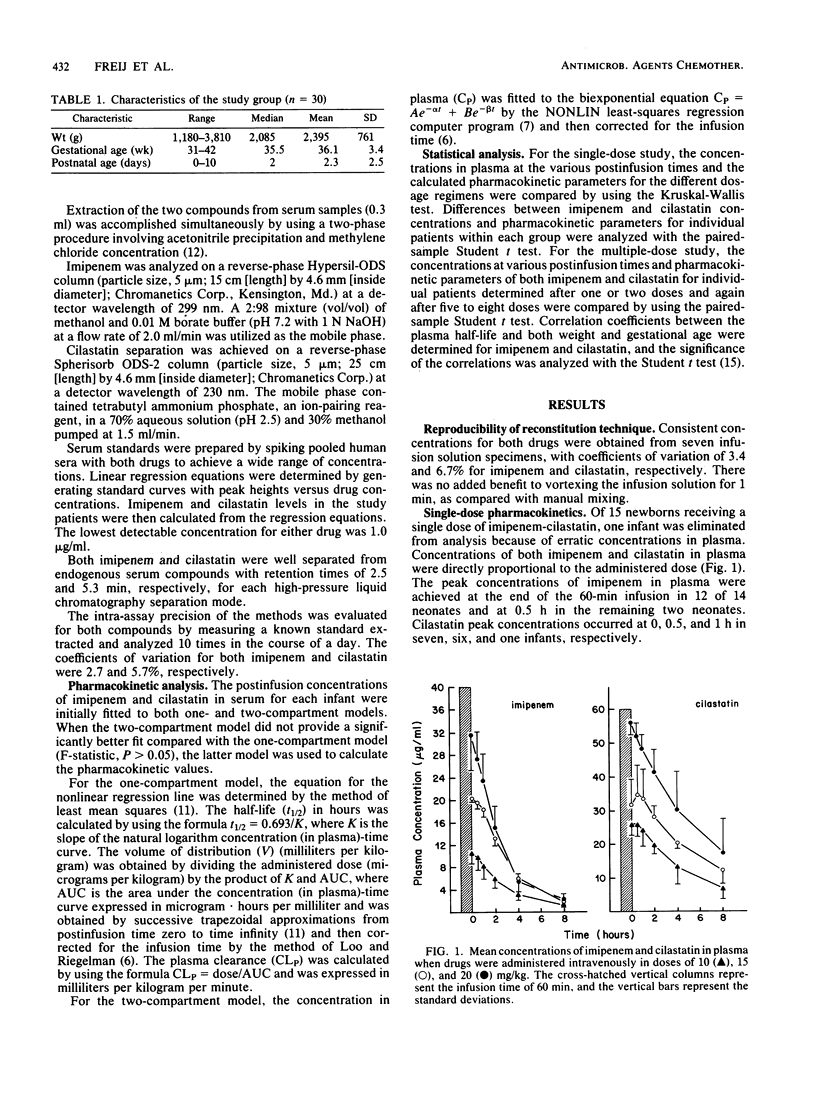
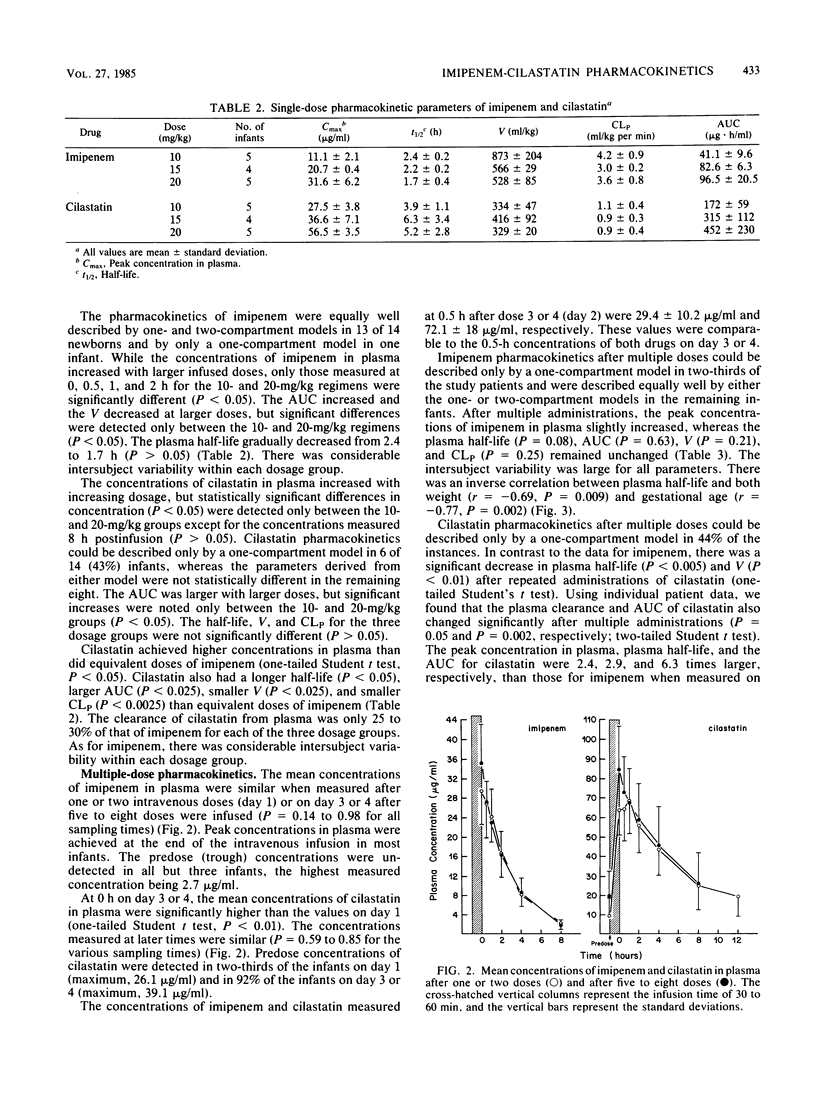
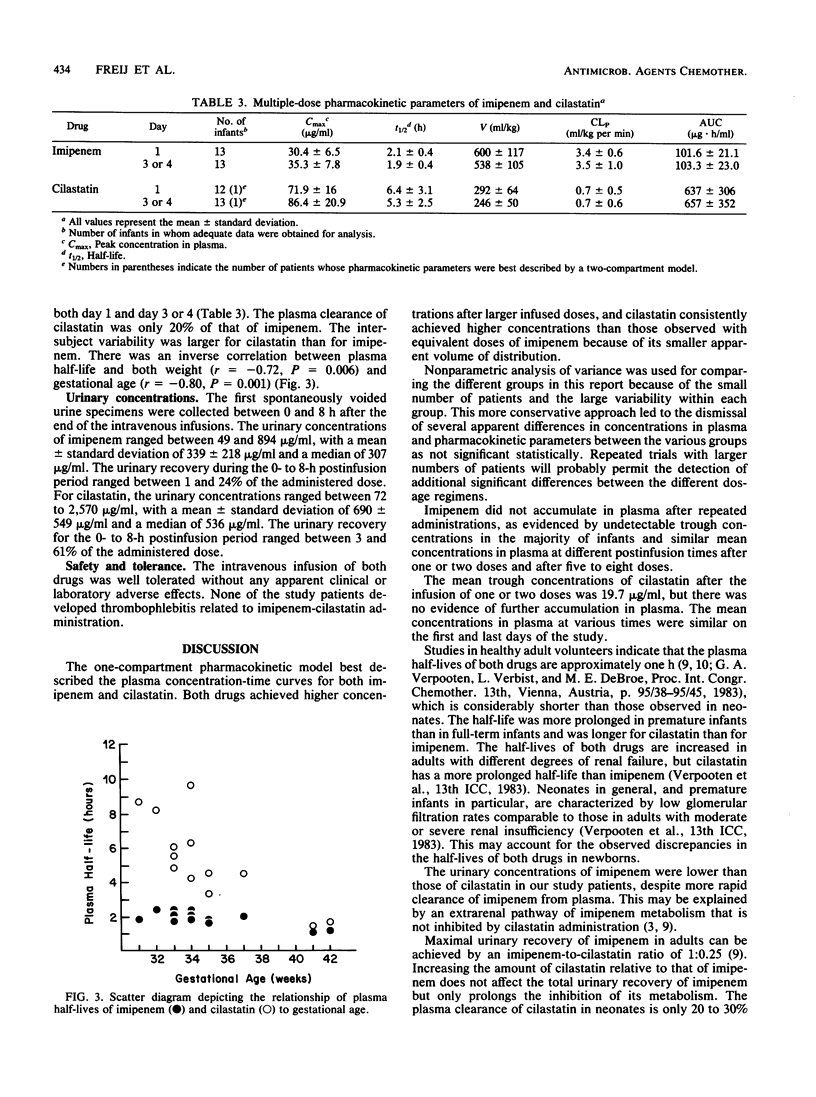
Imipenem and its renal dehydropeptidase I inhibitor, cilastatin, were coadministered intravenously in a 1:1 ratio to 30 newborns. Five infants each received single doses of 10, 15, or 20 mg/kg of both drugs. Concentrations in plasma were proportional to the administered dose, and cilastatin achieved consistently higher concentrations than did equivalent doses of imipenem because of its smaller volume of distribution. The pharmacokinetics of both drugs were best described by a one-compartment model. The plasma half-lives of imipenem were 1.7 to 2.4 h, whereas those of cilastatin were 3.9 to 6.3 h. The plasma clearance of cilastatin was approximately one-quarter of that of imipenem in the dose range tested. The urinary concentrations of imipenem were 50% of those of cilastatin despite its higher clearance from plasma. Fifteen additional newborns received five to eight doses of imipenem-cilastatin at 20 mg/kg per dose every 12 h. There was no accumulation of either drug in plasma after repeated administrations, and the mean concentrations in plasma were similar when measured on the first and last days of the multiple-dose study. There was marked intersubject variability, more so for cilastatin. The pharmacokinetics of both drugs in neonates resembled those observed in adults with moderate to severe renal insufficiency. Because the effects of enzyme inhibition on neonates are unknown, additional studies with imipenem-cilastatin (primaxin) are recommended.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Acar J. F., Goldstein F. W., Kitzis M. D., Gutmann L. Activity of imipenem on aerobic bacteria. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1983 Dec;12 (Suppl 500):37–45. doi: 10.1093/jac/12.suppl_d.37. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aznar J., García Iglesias M. C., Perea E. J. Comparative activity of imipenem (N-formimidoyl thienamycin) on enterococci and its interactions with aminoglycosides. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1984 Feb;13(2):129–132. doi: 10.1093/jac/13.2.129. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahan F. M., Kropp H., Sundelof J. G., Birnbaum J. Thienamycin: development of imipenen-cilastatin. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1983 Dec;12 (Suppl 500):1–35. doi: 10.1093/jac/12.suppl_d.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kesado T., Hashizume T., Asahi Y. Antibacterial activities of a new stabilized thienamycin, N-formimidoyl thienamycin, in comparison with other antibiotics. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1980 Jun;17(6):912–917. doi: 10.1128/aac.17.6.912. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kropp H., Sundelof J. G., Hajdu R., Kahan F. M. Metabolism of thienamycin and related carbapenem antibiotics by the renal dipeptidase, dehydropeptidase. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1982 Jul;22(1):62–70. doi: 10.1128/aac.22.1.62. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loo J. C., Riegelman S. Assessment of pharmacokinetic constants from postinfusion blood curves obtained after I.V. infusion. J Pharm Sci. 1970 Jan;59(1):53–55. doi: 10.1002/jps.2600590107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neu H. C., Labthavikul P. Comparative in vitro activity of N-formimidoyl thienamycin against gram-positive and gram-negative aerobic and anaerobic species and its beta-lactamase stability. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1982 Jan;21(1):180–187. doi: 10.1128/aac.21.1.180. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norrby S. R., Alestig K., Björnegård B., Burman L. A., Ferber F., Huber J. L., Jones K. H., Kahan F. M., Kahan J. S., Kropp H. Urinary recovery of N-formimidoyl thienamycin (MK0787) as affected by coadministration of N-formimidoyl thienamycin dehydropeptidase inhibitors. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1983 Feb;23(2):300–307. doi: 10.1128/aac.23.2.300. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norrby S. R., Alestig K., Ferber F., Huber J. L., Jones K. H., Kahan F. M., Meisinger M. A., Rogers J. D. Pharmacokinetics and tolerance of N-formimidoyl thienamycin (MK0787) in humans. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1983 Feb;23(2):293–299. doi: 10.1128/aac.23.2.293. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tally F. P., Jacobus N. V. Susceptibility of anaerobic bacteria to imipenem. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1983 Dec;12 (Suppl 500):47–51. doi: 10.1093/jac/12.suppl_d.47. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welch C. L., Campbell B. J. Uptake of glycine from L-alanylglycine into renal brush border vesicles. J Membr Biol. 1980;54(1):39–50. doi: 10.1007/BF01875375. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


