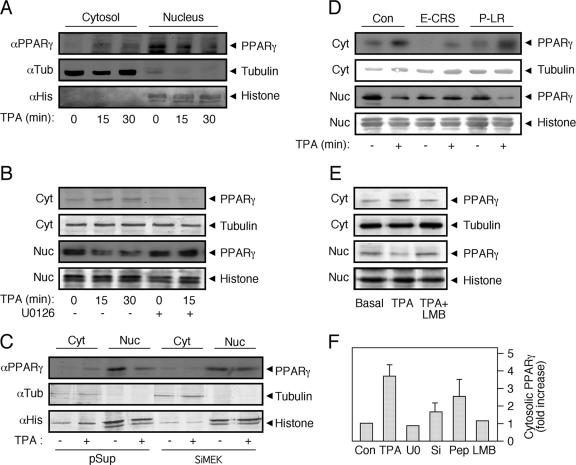
FIG. 9.
PPARγ nuclear export is mediated by MEKs. Subconfluent, serum-starved (0.1% FCS, 16 h) HeLa cells were treated as follows: (A) stimulated with TPA (250 nM, 15 and 30 min) or left untreated; (B) stimulated with TPA (250 nM, 15 and 30 min) or pretreated with U0126 (5 μM) 15 min prior to addition of TPA (250 nM, 15 min) or vehicle control. (C) HeLa cells were transiently transfected with combination of 4 siRNA vectors of MEK1 and 2 (SiMEK) or with vector (pSuper) control. Four days after transfections, the cells were serum starved for 16 h and treated with TPA (250 nM, 15 min) (+) or left untreated (−). (D) HeLa cells were preincubated for 45 min with interfering cell-permeable peptide CRSPerE (E-CRS) or the control permeable peptide LRPerP (P-LR) or left untreated, followed by TPA stimulation (250 nM, 15 min). (E) HeLa cells were treated with TPA (250 nM, 15 min) or with LMB (5 ng/ml, 60 min) plus TPA (250 nM, 15 min) or left untreated. All treated cells were extracted and subjected to cellular fractionation as described. The lysates were Western blotted with PPARγ Ab and with tubulin Ab and histone H1 (histone) Ab as markers for the cytosolic (Cyt) and nuclear (Nuc) fractions, respectively. (F) The amount of PPARγ in the cytosol was quantitated using densitometry, and the results are shown in a bar graph (n = 3).