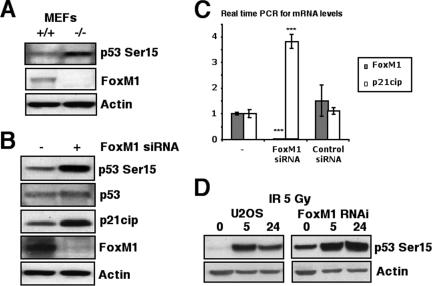
FIG. 2.
FoxM1-deficient cells exhibit increased activation of the p53 tumor suppressor. (A and B) FoxM1-deficient cells exhibited increased phosphorylation of serine 15 of the p53 tumor suppressor protein. (A) Cell extracts were prepared from wild type (+/+) or FoxM1−/− (−/−) MEFs, and levels of p53 Ser15 phosphorylation (top), FoxM1 (middle), and β-actin (bottom) were analyzed by Western blotting. (B) Also, cell extracts prepared from FoxM1 siRNA-transfected U2OS cells (+) or control cells (−) were analyzed by Western blotting for levels of p53 Ser15 phosphorylation, p53, p21Cip1 (downstream target gene of p53), FoxM1, and β-actin. (C) Increased levels of p21Cip1 mRNA were found in FoxM1-deficient U2OS cells. U2OS cells were transfected with FoxM1 siRNA or control siRNA, and then 72 h later, RNA was prepared to examine for expression of p21Cip1 mRNA by qRT-PCR. The asterisks indicate statistically significant changes: ***, P ≤ 0.001. (D) FoxM1-deficient U2OS cells show increased phosphorylation of serine 15 of the p53 tumor suppressor protein in response to γ-irradiation. U2OS cells were transfected with or without FoxM1 siRNA and then exposed 5 Gy of IR. Cell extracts were prepared at 0 h, 5 h, or 24 h post-IR and analyzed by Western blotting for levels of p53 Ser15 phosphorylation (top) and β-actin (bottom).