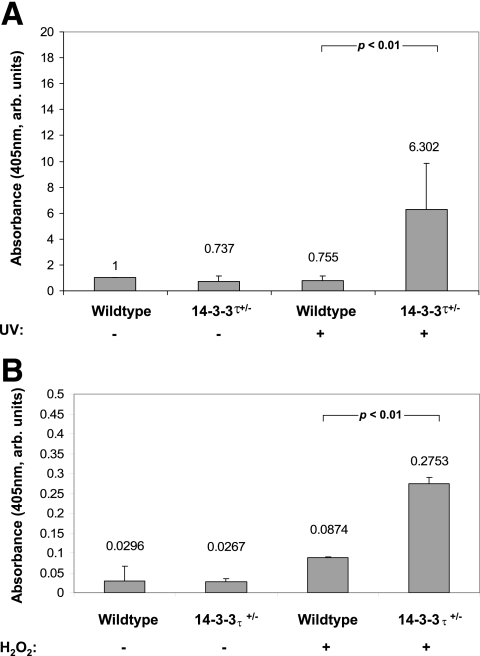
FIG. 2.
Increased apoptosis in adult murine cardiomyocytes obtained from 14-3-3τ+/− mice. A. Adult cardiomyocytes were isolated from 14-3-3τ+/− and wild-type 10- to 12-week-old mice and treated with UVC irradiation (180 J/m2), a well-described stimulus of apoptosis. 14-3-3τ+/− cardiomyocytes displayed an approximately eightfold-higher rate of apoptosis than wild-type cells in response to UVC irradiation (6.30% ± 3.50% for 14-3-3τ+/− mice versus 0.76% ± 0.37% for wild-type mice; P < 0.05; see Fig. 4A). B. 14-3-3τ+/− cardiomyocytes were also sensitized to H2O2-induced apoptosis. Treatment of cells with 10 μM of H2O2 for 12 h caused 14-3-3τ+/− cardiomyocytes to undergo apoptosis at an approximately 3.5-fold-higher rate than wild-type cardiomyocytes (0.2753% ± 0.0154% for 14-3-3τ+/− mice versus 0.0874% ± 0.002% for wild-type mice; P < 0.05; see Fig. 4B). arb. units, arbitrary units.