FIG.3.
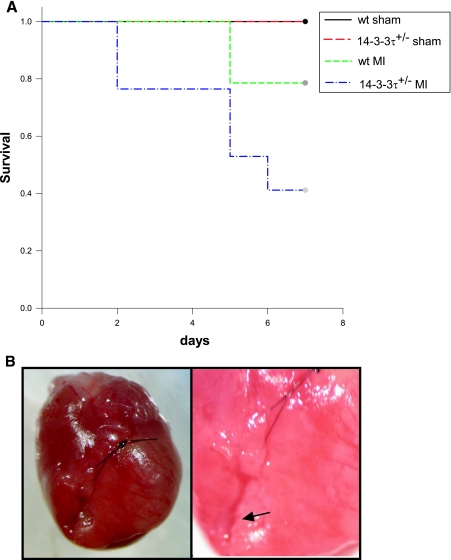
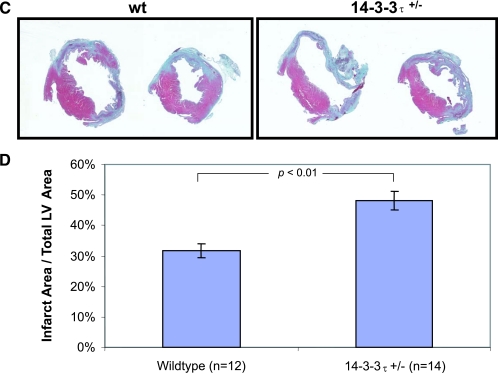
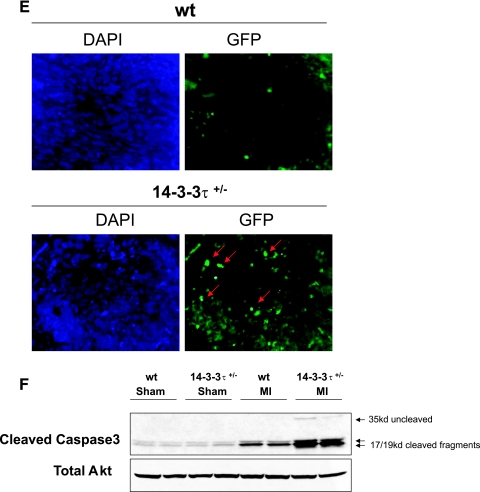
Increased cardiac remodeling after myocardial infarction in 14-3-3τ+/− mice. A. Kaplan-Meier survival analysis after myocardial infarction. 14-3-3τ+/− mice had much higher mortality 7 days following left coronary artery ligation. B. Ventricular free wall rupture occurs in 14-3-3τ+/− mice following myocardial infarction surgery. Hearts were isolated from mice and viewed with a dissecting microscope. The right panel depicts a close-up view of the site of rupture (arrow) in the same heart shown in the left panel. C. Histologic analysis of infarct size 7 days after ligation of the left coronary artery in wild-type and 14-3-3τ+/− mice. Hearts were isolated, fixed in formalin, embedded in paraffin, sectioned with a microtome, stained with trichrome, and analyzed by computerized microscopy. D. Quantitative analysis of histological sections described for panel B. The area of infarction was divided by the total left ventricular area in each section. Ten sections per heart were analyzed. E. Analysis of cardiomyocyte apoptosis in the infarct border zone by TUNEL. Hearts were isolated 7 days after myocardial infarction, fixed in formalin, embedded in paraffin, sectioned with a microtome, and analyzed by TUNEL. The infarct border zone was defined as one-quarter circumference of the left ventricle on either side of the infarct. F. Analysis of caspase-3 activation in ventricular tissue after myocardial infarction. Ventricles were isolated 7 days after myocardial infarction, minced, and used to obtain protein lysates. Protein lysates were separated by SDS-PAGE and analyzed by immunoblotting for cleaved caspase-3. Blots were reprobed for total Akt to control for loading.