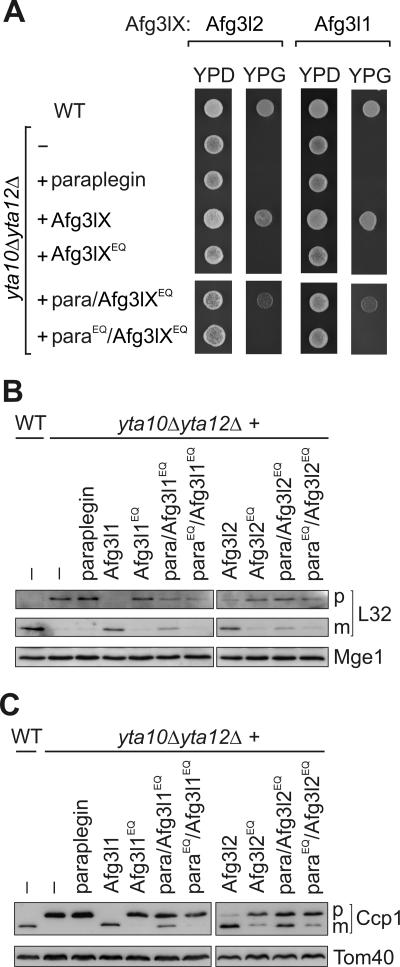
FIG. 6.
Proteolytic activity of homo-oligomeric and hetero-oligomeric m-AAA protease complexes in yeast. (A) Respiratory growth of yta10Δ yta12Δ cells expressing murine m-AAA protease subunits. Wild-type (WT) cells, yta10Δ yta12Δ cells, and yta10Δ yta12Δ cells expressing either paraplegin, Afg3l1 (Afg3lX), Afg3l2 (Afg3lX), or their mutant variants Afg3l1E567Q or Afg3l2E574Q (Afg3lXEQ) were grown at 30°C on glucose-containing (YPD) or glycerol-containing (YPG) media to examine the respiratory competence of the cells. To assess the activity of hetero-oligomeric complexes, the mutant variants Afg3l1E567Q or Afg3l2E574Q were coexpressed with paraplegin (para/Afg3lXEQ) or with parapleginE575Q (paraEQ/Afg3lXEQ) in yta10Δ yta12Δ cells and cell growth was analyzed as above. (B and C) Processing of yeast MrpL32 and Ccp1 by murine m-AAA proteases. Protein processing was analyzed in yta10Δ yta12Δ cells harboring murine m-AAA protease subunits by SDS-PAGE as described for panel A and immunoblotting as described in the legend for Fig. 1 by using MrpL32 (L32)-specific antisera (B) or Ccp1-specific antisera (C). p, precursor forms; m, mature forms. Mge1 and Tom40 were used to control for equal gel loading.