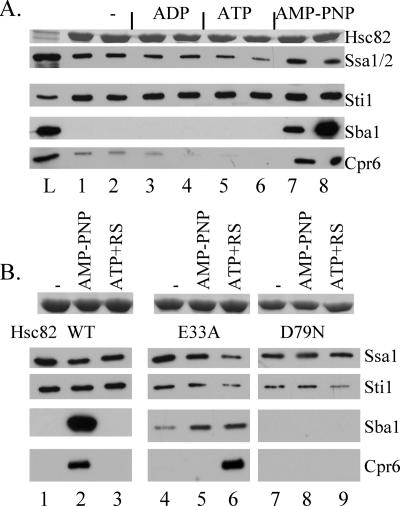
FIG. 1.
Interaction of cochaperone proteins with WT His-tagged Hsc82 and His-Hsc82 containing alterations of residues required for ATP binding and hydrolysis. A. Cell extracts were prepared from cells expressing His-Hsc82 as the only Hsp90 protein in the cell and supplemented with no exogenous nucleotide (lanes 1 and 2), 5 mM ADP (lanes 3 and 4), 5 mM ATP (lanes 5 and 6), or AMP-PNP (lanes 7 and 8). His-Hsc82 complexes were isolated after a 5-min incubation on ice (odd-number lanes) or at 30°C (even-number lanes). L, whole-cell extract. B. Cell extracts were prepared from cells expressing His-Hsc82 WT, -E33A, or -D79N along with WT untagged Hsp82. His-Hsc82 complexes were isolated from lysates incubated for 5 min at 30°C in the presence of no exogenous nucleotide (lanes 1, 4, and 7), 5 mM AMP-PNP (lanes 2, 5, and 8), or 5 mM ATP plus an ATP-regenerating system (ATP+RS, lanes 3, 6, and 9). Lanes 1 to 3, WT His-Hsc82; lanes 4 to 6, His-Hsc82-E33A; lanes 7 to 9, His-Hsc82-D79N. Nickel resin-bound protein complexes were separated by SDS-PAGE followed by Coomassie blue staining or immunoblot analysis. The Coomassie blue-stained band corresponding to His-Hsc82 is shown in the upper panel, and the lower panels represent immunoblot analysis using antibodies against the indicated proteins.