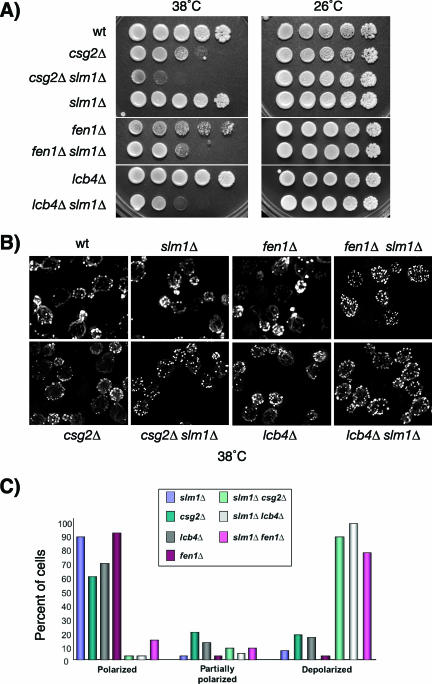
FIG. 3.
Synthetic genetic interactions between slm1Δ mutants and mutants with mutations in the sphingolipid biosynthesis pathway. (A) Serial dilutions of isogenic wild-type, slm1Δ, csg2Δ, fen1Δ, and lcb4Δ single-mutant, and slm1Δ csg2Δ, slm1Δ fen1Δ, and slm1Δ lcb4Δ double-mutant yeast cultures were spotted on YPD plates. Plates were incubated at 26°C and 38°C and photographed after 3 days. (B) Exponentially growing wild-type, slm1Δ, csg2Δ, fen1Δ, and lcb4Δ single-mutant and slm1Δ csg2Δ, slm1Δ fen1Δ, and slm1Δ lcb4Δ double-mutant yeast cultures grown at 26°C were shifted to 38°C for 2 h. Cells were fixed and stained with Alexa594-phalloidin to visualize the actin cytoskeleton. (C) Small- to medium-budded cells from panel B were scored for their actin polarization state. Cells were classified as having an actin cytoskeleton that was polarized (containing cables and polarized actin patches), partially polarized (containing cables and partially polarized patches), or depolarized (containing no cables and depolarized patches). One hundred cells per sample were counted.