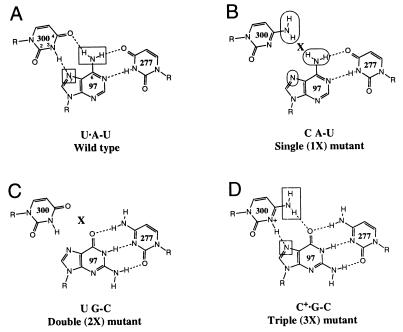
Figure 2.
Wild-type and mutant ribozyme base triples involving nucleotides 300, 97, and 277. Functional groups assayed by NAIM are indicated by rectangles (interference) and ovals (enhancement). (A) Wild-type Tetrahymena intron base triple, U300⋅A97-U277, in which the H3 of U300 hydrogen bonds with the N7 of A97, and the O4 of U300 hydrogen bonds with the N6 amine of A97. Both the N7 and N6 positions show interference in the wild-type ribozyme (11). (B) U300C (1X) mutant. By replacing U300 with a C, the interaction with the Hoogsteen face of A97 is perturbed. (C) A97G + U277C (2X) mutant. The base triple is disrupted by replacing the A97-U277 base pair with a Watson-Crick G-C pair. (D) U300C + A97G − U277C (3X) mutant. This set of mutations restores the predicted base triple with an isomorphous triple that is the next most phylogenetically conserved sequence in the IC1 and IC2 intron subgroups (11). In every case that U300 is changed to a C within these subgroups, the A97-U277 base pair co-varies as a G-C pair.