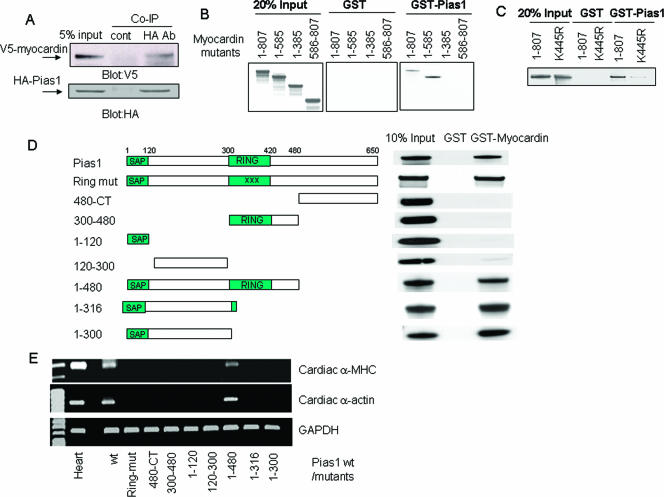
FIG. 5.
Protein regions responsible for the physical interaction between PIAS1 and myocardin. (A) Total extracts from CV1 cells transfected with V5-tagged myocardin and HA epitoped PIAS1 were coimmunoprecipitated (Co-IP) with a control (cont) antibody (Ab) and HA antibody, respectively. Protein Western blots were revealed by staining with V5 antibody (upper panel) or HA antibody (lower panel). (B and C) Amino acid residues 385 to 586 contributed to the physical interaction with PIAS1. In vitro-translated 35S-labeled serial deletion or point mutants of myocardin were incubated with either GST or GST-fused PIAS1 and precipitated by GST beads. (D) The N-terminal region of PIAS1 physically interacted with myocardin. In vitro-translated 35S-labeled serial deletion mutants of PIAS1 were incubated with either GST or GST-fused myocardin and precipitated by GST beads. (E) Both the RING domain and the protein-interacting region in PIAS1 were required by myocardin to activate cardiogenic gene expression. The expression of selected cardiac muscle-specific genes were determined by RT-PCR on total RNAs from 10T1/2 fibroblast cells transfected with myocardin along with the indicated one serial deletion mutant of PIAS1. All data shown represent at least two independent assays. wt, wild type; mut, mutant; CT, C terminus.