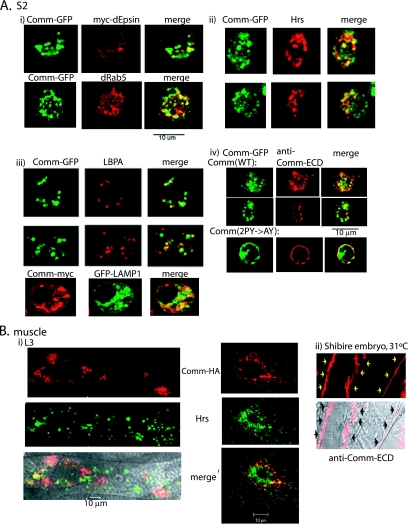
FIG. 3.
WT Comm internalizes from the plasma membrane and colocalizes with endocytic markers. (A) Drosophila S2 cells were cotransfected with Comm-GFP and myc-dEpsin, immunostained with anti-myc antibodies, and analyzed by confocal microscopy for colocalization of Comm and dEpsin at the PM and in early endosomes. Colocalization of Comm-GFP with the early endosomal marker dRab5 is shown as well (panel i). Panel ii depicts colocalization of endogenous Hrs (marking early and maturing endosomes) and transfected Comm-GFP in S2 cells, and panel iii depicts colocalization of endogenous LBPA or transfected LAMP1 (marking late endosomes/lysosomes) with transfected Comm in these cells. Panel iv demonstrates immunostaining with antibodies directed to the extracellular domain (ECD) of Comm of live (nonpermeabilized) S2 cells transfected with Comm-GFP. Note the accumulation of WT Comm in vesicles following their internalization from the PM (upper panel) and the accumulation of the Comm(2PY→AY) mutant at the PM (lower panel). (B) Panel i shows muscles dissected from third-instar larvae of UAS-comm+/24B-GAL4 flies and coimmunostained with anti-HA antibodies (to detect the HA-tagged Comm) and anti-Hrs antibodies and analyzed by confocal microscopy. The left panel depicts a muscle section, and the right panel represents a higher magnification of a muscle segment. The bottom left panel shows a confocal image overlaid over a differential interference contrast image. Panel ii shows endogenous Comm, stained with anti-Comm-ECD, accumulating in muscle surface of stage 17 embryos of shibire mutants grown at the nonpermissive temperature (31°C) to block internalization of PM proteins. Arrows mark the surface of two muscles.