Figure 1.
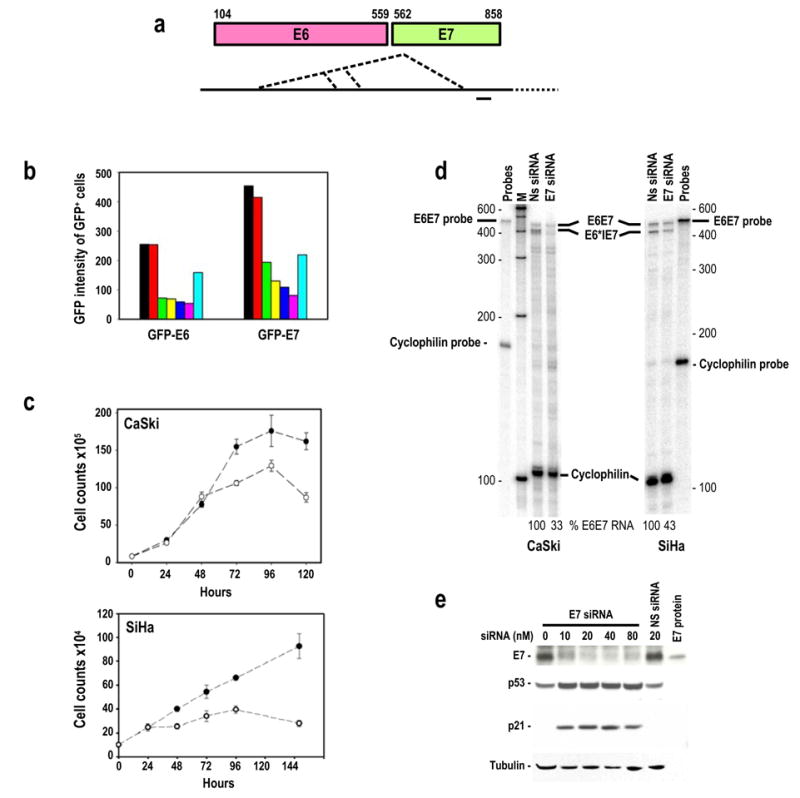
Suppression of HPV16 E6 and E7 expression by transient transfection of HPV16 E7 siRNA. (a) Diagram of HPV16 E6 and E7 gene structure (colored boxes) and their bicistronic transcripts (long heavy line) with alternative splice sites as depicted by the dotted lines. A small heavy dash immediately below the transcript indicates the region targeted by the E7 siRNA 198 duplex in this study. (b) Inhibition of GFP-E6 and GFP-E7 expression in 293 cells by co-transfection of GFP-E6 or GFP-E7 expression vector (1 μg/dish) with no siRNA (black), 20 nM non-specific (NS) siRNA (red), 10 (green), 20 (yellow), 40 (blue), or 80 nM (magenta) E7 siRNA, or 20 nM GFP siRNA (sky blue) as analyzed by flow cytometry. (c) Growth inhibition of cervical cancer–derived HPV16+ CaSki and SiHa cells in the presence of 40 nM E7 siRNA (open circles) or NS siRNA (closed circles). (d) HPV16 E7 siRNA-mediated degradation of HPV16 E6E7 RNAs in cervical cancer–derived CaSki and SiHa cells as analyzed by RPA. Total cell RNA was prepared after 24 hours of transfection with 20 nM E7 siRNA or NS siRNA. Cellular cyclophilin RNA was used for normalization of sampling as described (Tang and Zheng, 2002). (e) Inhibition of HPV16 E7 expression and accumulation of p53 and p21 proteins in CaSki cells 48 hours after transfection with HPV16 E7 siRNA or NS siRNA. HPV16 E7 protein is an E7 protein expressed from bacteria used as a control for the Western blot.
