Figure 1.
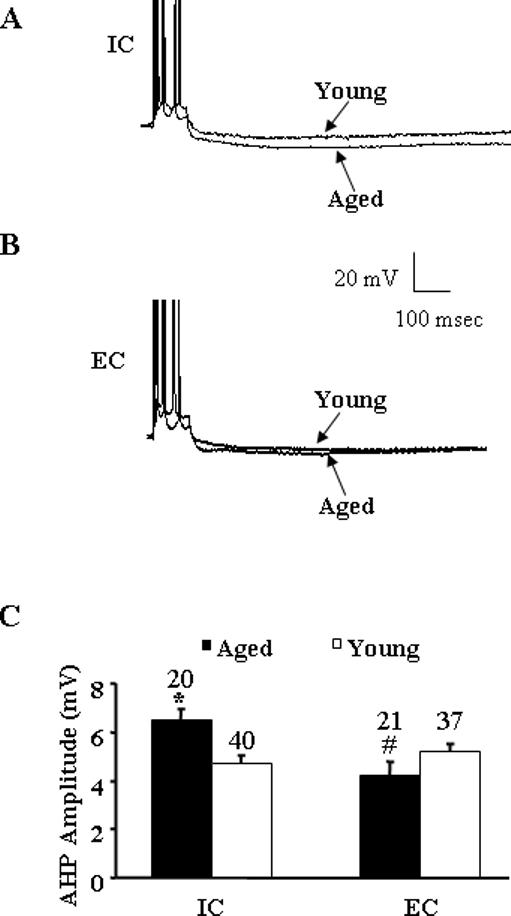
A: Representative voltage records from CA1 pyramidal cells from aged and young rats exposed to individual cages (IC). The AHP is evoked after a train of four action potentials, elicited by a 100-ms pulse of depolarizing current. Both cells were held at −62 mV. Note that action potentials are truncated to better illustrate the AHPs. B: Representative voltage records from CA1 pyramidal cells from aged and young rats exposed to environmental enrichment conditions (EC). Again the AHP is evoked after a train of four action potentials elicited by a 100-ms pulse of depolarizing current and the cells were held at −61 mV. C: Mean AHP amplitude (mV) recorded in neurons of aged (filled bars) and young (open bars) rats exposed to IC and EC. Asterisk indicates a significant increase (P < 0.005) in AHP amplitude in aged rats compared to young rats in IC group. Pound sign indicates a significant decrease (P < 0.005) in AHP amplitude in EC aged compared to IC aged rats. Number above each bar indicates number of cells recorded in each group.
