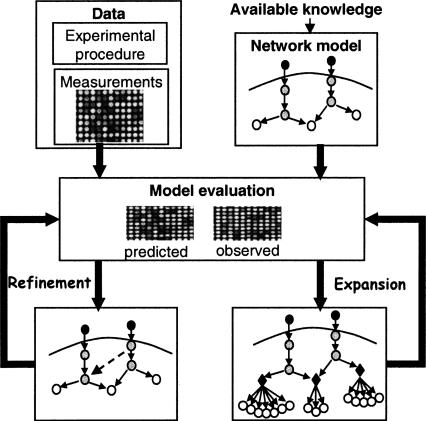
Figure 1.
Overview of the model improvement methodology. Model formalization: The current qualitative knowledge on the studied biological system is formalized as a Bayesian network (top right; see also Fig. 2). The illustrated model contains several molecular types: environmental stimulations (dark gray), signaling proteins and transcription factors (light gray), and mRNAs (white). The refinement and expansion procedures take as input the network model and high throughput measurements on network's components (top left), and search systematically for model improvements that maximize a probabilistic improvement score. The score measures the increase of fit between the model predictions and the observed data. The model refinement procedure (middle left) seeks structural and logical changes in existing model components, which attain the best score. Structural refinements are marked by dashed connections. The model expansion procedure (middle right) assigns systematically new target genes to regulatory modules, based on their fit to the predicted expression of the module. In the illustration, three regulatory modules were formed. They contain known and novel target genes (white circles). All genes in the same module share the same logic (black diamonds).