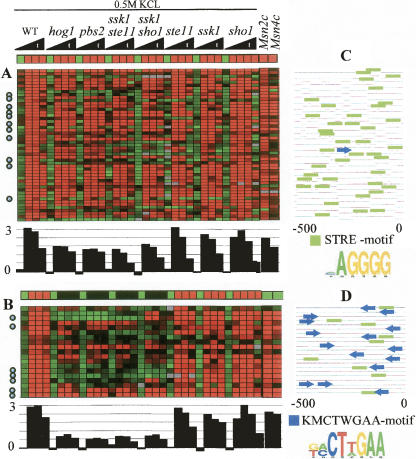
Figure 5.
Expression profiles of two modules associated with Msn2/4. (A) The known Msn2/4 module. (B) The novel Hog1A module. The conditions are time series measurements in response to 0.5 M KCl osmotic shock. Below the predicted expression vector and the observed expression matrix (the same presentation as in Fig. 4), the average fold induction of the module is shown. Both modules are hypothesized to be regulated by Msn2/4 and include many known Msn2/4 targets (marked with circles). However, their expression patterns are clearly distinct: The Hog1A module depends much more strongly on the presence of Hog1 in severe osmotic shock. In wild type (WT), the expression level in both modules is ∼3, but in hog1, pbs2, ssk1ste11, and ssk1sho1 the expression levels differ significantly: ∼0.5 in Hog1A and ∼2 in Msn2/4 module (KS-test P-value < 10−4). The two rightmost columns in A and B show the expression level of the modules in Msn2 and Msn4 overexpression mutants. Although the predicted expression in these conditions is low in the Hog1A module, the observed level in both modules is high, indicating that both modules are regulated by Msn2/4. (C,D) Promoter analysis. Each line represents the 500-bp sequence upstream of the transcription start site for the gene in that row. Green boxes represent occurrences of the STRE motif (a known Msn2/4 binding site); blue arrows represent the new motif KMCTWGAA discovered in this analysis. This motif exhibits a non-uniform distribution along the promoter in terms of location and orientation. The novel motif supports the separation of the Msn2/4 targets into two distinct modules.