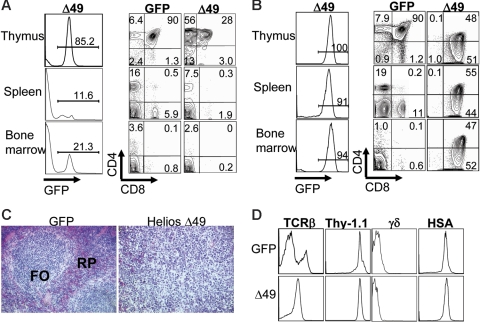
Figure 5.
Expression of the Helios Δ49-285 isoform results in T-cell lymphoma. (A) FACS analysis of hematolymphoid tissues in a nonsick Helios Δ49-285 animal at 5 months after transplantation showing an abnormal frequency of CD4 SP thymocytes among cells that are GFP+. The abnormal accumulation of CD4+ (or CD8+ in some cases) cells was restricted to the thymus at early stages of lymphoma. The extent of GFP chimerism in each tissue for the nonsick Δ49-285 Helios animal is shown in the left column. (B) FACS analysis of a moribund Helios Δ49-285 animal at 7 months after transplantation indicating high frequencies of GFP+ cells in the thymus and abnormal accumulation of DP and CD8 SP thymocytes in the spleen and bone marrow. Numbers in the quadrants of each plot represent percentages of the indicated populations among gated GFP+ cells. (C) Splenic architecture was severely disrupted in animals exhibiting lymphoma. FO indicates lymphoid follicle; RP, red pulp; original magnification, × 160. (D) Characterization of cell-surface marker profiles of lymphoma cells in the thymus of a representative moribund Δ49-285 Helios animal (n = 5) versus the GFP control. Analysis was done on gated GFP+ cells.