Abstract
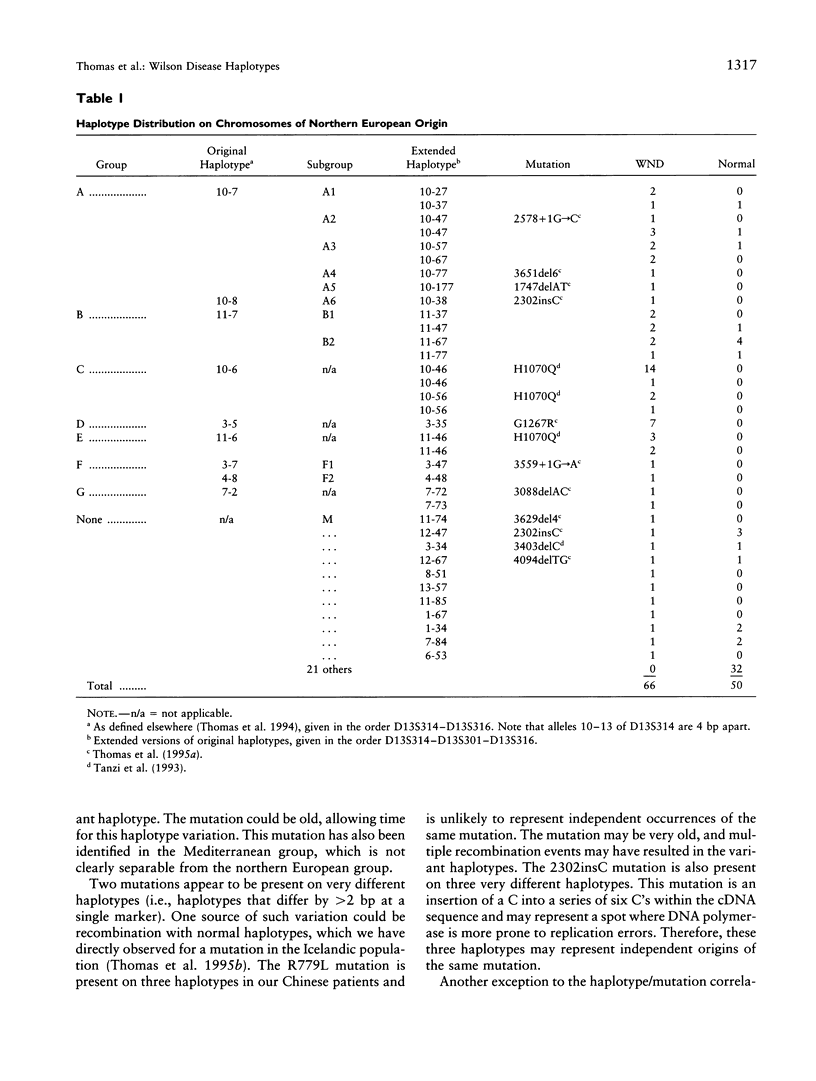
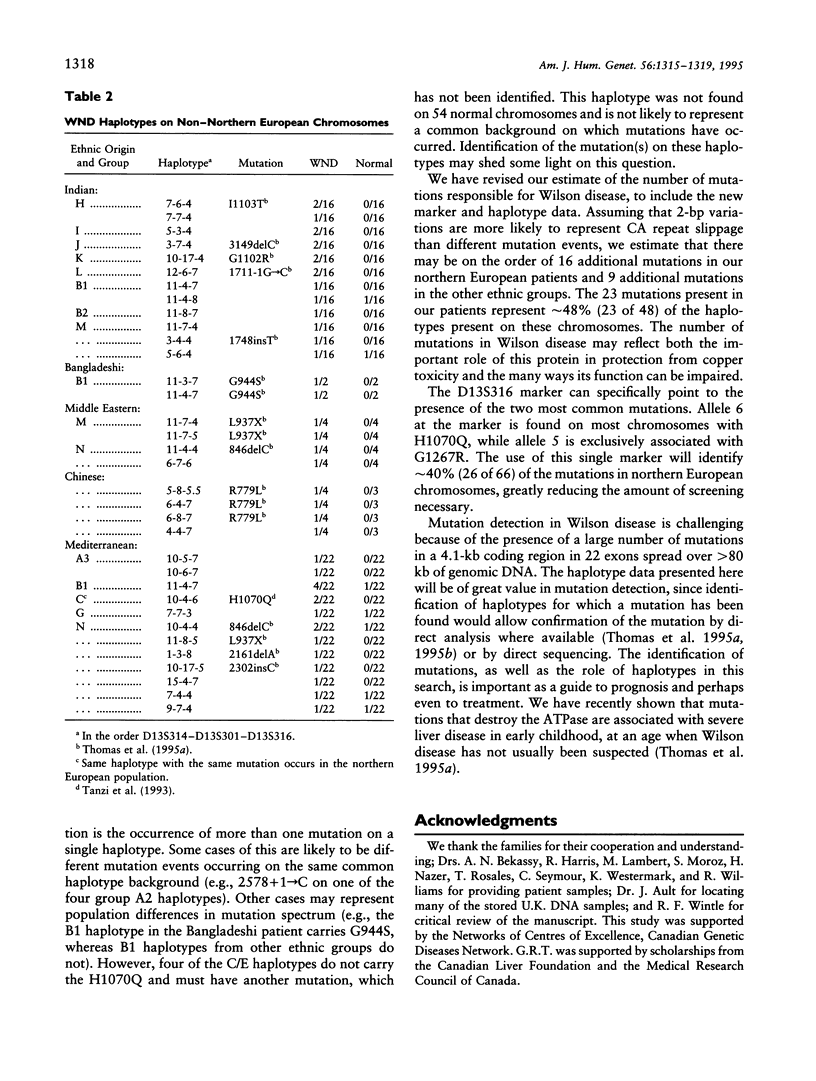
Wilson disease is a disorder of copper transport, resulting in neurological and hepatic damage due to copper toxicity. We have recently identified > 20 mutations in the copper-transporting ATPase defective in this disease. Given the difficulties of searching for mutations in a gene spanning > 80 kb of genomic DNA, haplotype data are important as a guide to mutation detection. Here we examine the haplotypes associated with specific mutations. We have extended previous studies of DNA haplotypes of dinucleotide-repeat polymorphisms (CA repeats) in the Wilson disease region to include an additional marker, in 58 families. These haplotypes, combining three markers (D13S314, D13S316, and D13S301), are usually specific for each different mutation, even though highly polymorphic CA repeat markers have been used. Haplotypes, as well as their accompanying mutations, differ between populations. In the patients whom we have studied, the haplotype data indicate that as many as 20 mutations may still be unidentified. The use of the haplotypes that we have identified provides an important guide for the identification of known mutations and can facilitate future mutation searches.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bonné-Tamir B., Frydman M., Agger M. S., Bekeer R., Bowcock A. M., Hebert J. M., Cavalli-Sforza L. L., Farrer L. A. Wilson's disease in Israel: a genetic and epidemiological study. Ann Hum Genet. 1990 May;54(Pt 2):155–168. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-1809.1990.tb00372.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bull P. C., Thomas G. R., Rommens J. M., Forbes J. R., Cox D. W. The Wilson disease gene is a putative copper transporting P-type ATPase similar to the Menkes gene. Nat Genet. 1993 Dec;5(4):327–337. doi: 10.1038/ng1293-327. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houwen R. H., Roberts E. A., Thomas G. R., Cox D. W. DNA markers for the diagnosis of Wilson disease. J Hepatol. 1993 Mar;17(3):269–276. doi: 10.1016/s0168-8278(05)80204-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houwen R. H., van Hattum J., Hoogenraad T. U. Wilson disease. Neth J Med. 1993 Aug;43(1-2):26–37. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McClatchey A. I., Trofatter J., McKenna-Yasek D., Raskind W., Bird T., Pericak-Vance M., Gilchrist J., Arahata K., Radosavljevic D., Worthen H. G. Dinucleotide repeat polymorphisms at the SCN4A locus suggest allelic heterogeneity of hyperkalemic periodic paralysis and paramyotonia congenita. Am J Hum Genet. 1992 May;50(5):896–901. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller S. A., Dykes D. D., Polesky H. F. A simple salting out procedure for extracting DNA from human nucleated cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Feb 11;16(3):1215–1215. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.3.1215. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oudet C., Mornet E., Serre J. L., Thomas F., Lentes-Zengerling S., Kretz C., Deluchat C., Tejada I., Boué J., Boué A. Linkage disequilibrium between the fragile X mutation and two closely linked CA repeats suggests that fragile X chromosomes are derived from a small number of founder chromosomes. Am J Hum Genet. 1993 Feb;52(2):297–304. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petrukhin K., Fischer S. G., Pirastu M., Tanzi R. E., Chernov I., Devoto M., Brzustowicz L. M., Cayanis E., Vitale E., Russo J. J. Mapping, cloning and genetic characterization of the region containing the Wilson disease gene. Nat Genet. 1993 Dec;5(4):338–343. doi: 10.1038/ng1293-338. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sirugo G., Keats B., Fujita R., Duclos F., Purohit K., Koenig M., Mandel J. L. Friedreich ataxia in Louisiana Acadians: demonstration of a founder effect by analysis of microsatellite-generated extended haplotypes. Am J Hum Genet. 1992 Mar;50(3):559–566. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanzi R. E., Petrukhin K., Chernov I., Pellequer J. L., Wasco W., Ross B., Romano D. M., Parano E., Pavone L., Brzustowicz L. M. The Wilson disease gene is a copper transporting ATPase with homology to the Menkes disease gene. Nat Genet. 1993 Dec;5(4):344–350. doi: 10.1038/ng1293-344. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas G. R., Bull P. C., Roberts E. A., Walshe J. M., Cox D. W. Haplotype studies in Wilson disease. Am J Hum Genet. 1994 Jan;54(1):71–78. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas G. R., Forbes J. R., Roberts E. A., Walshe J. M., Cox D. W. The Wilson disease gene: spectrum of mutations and their consequences. Nat Genet. 1995 Feb;9(2):210–217. doi: 10.1038/ng0295-210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas G. R., Jensson O., Gudmundsson G., Thorsteinsson L., Cox D. W. Wilson disease in Iceland: a clinical and genetic study. Am J Hum Genet. 1995 May;56(5):1140–1146. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas G. R., Roberts E. A., Rosales T. O., Moroz S. P., Lambert M. A., Wong L. T., Cox D. W. Allelic association and linkage studies in Wilson disease. Hum Mol Genet. 1993 Sep;2(9):1401–1405. doi: 10.1093/hmg/2.9.1401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


