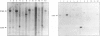Abstract
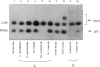
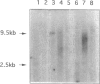
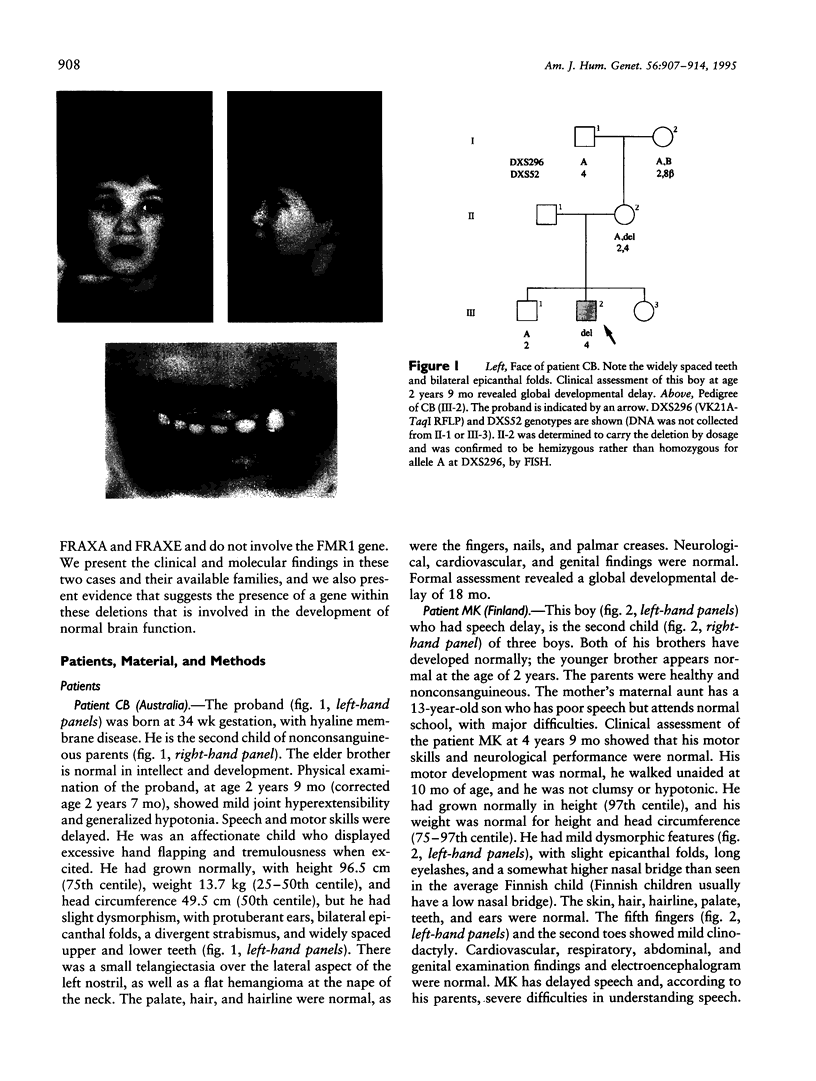
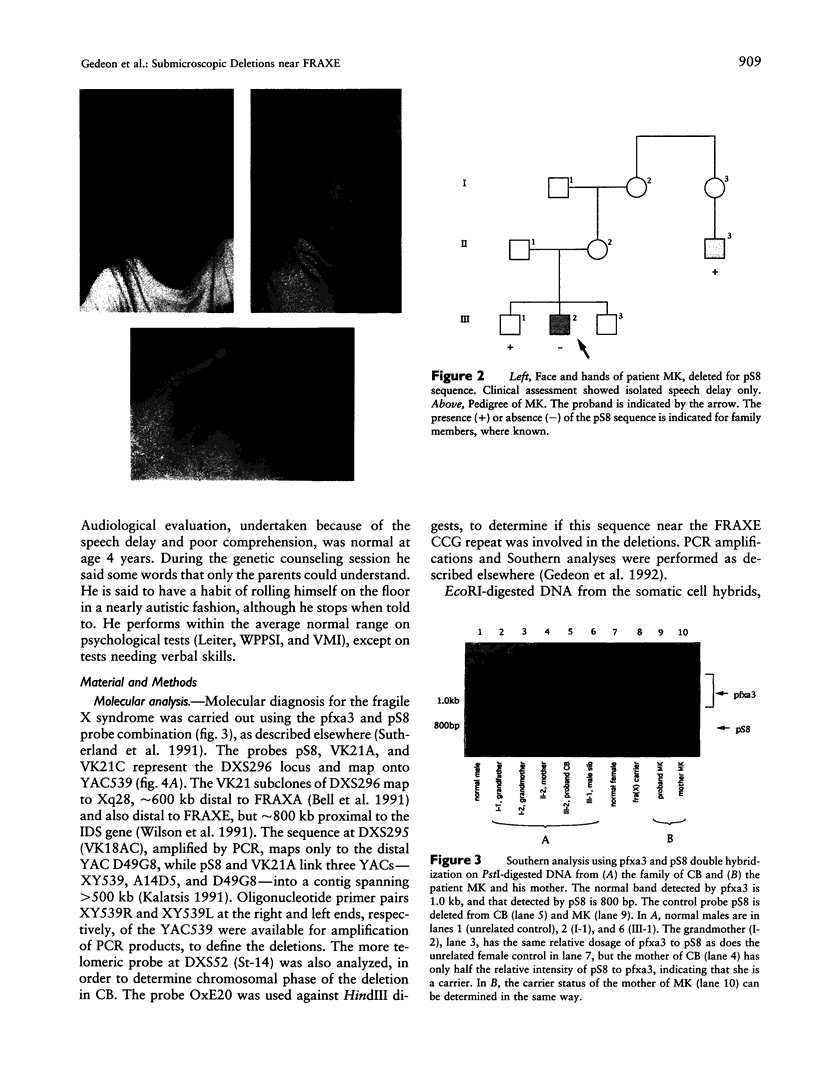
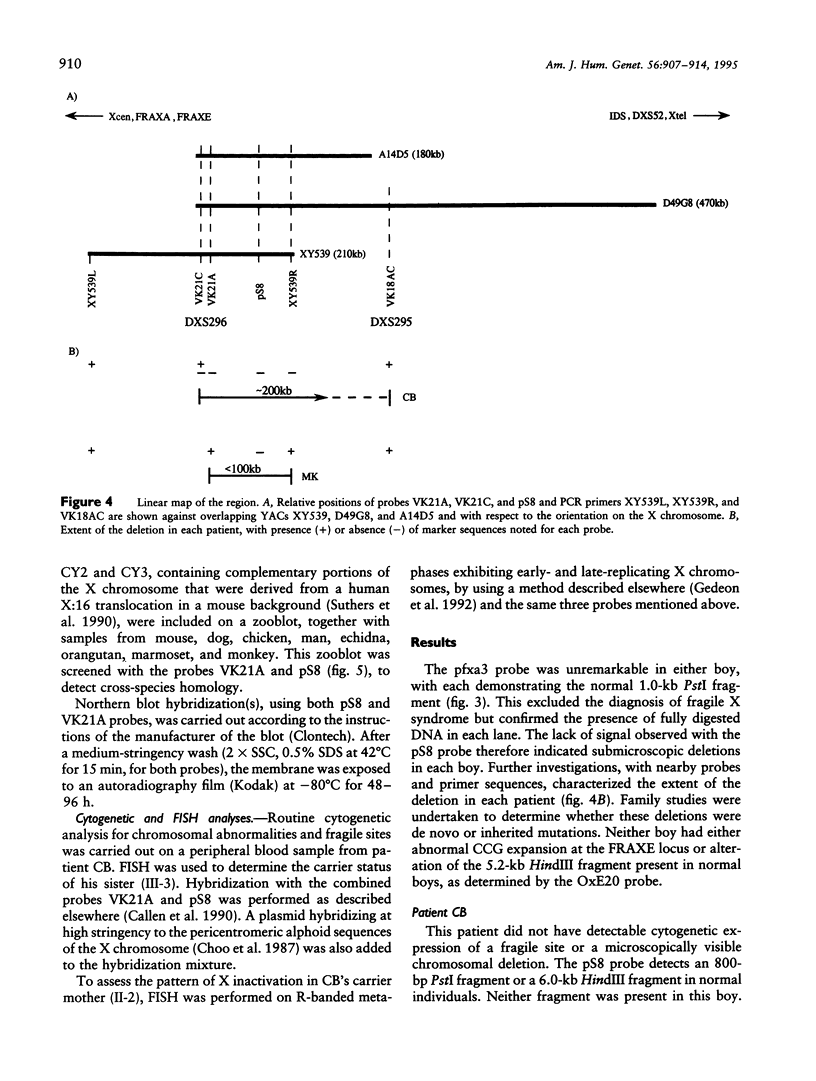
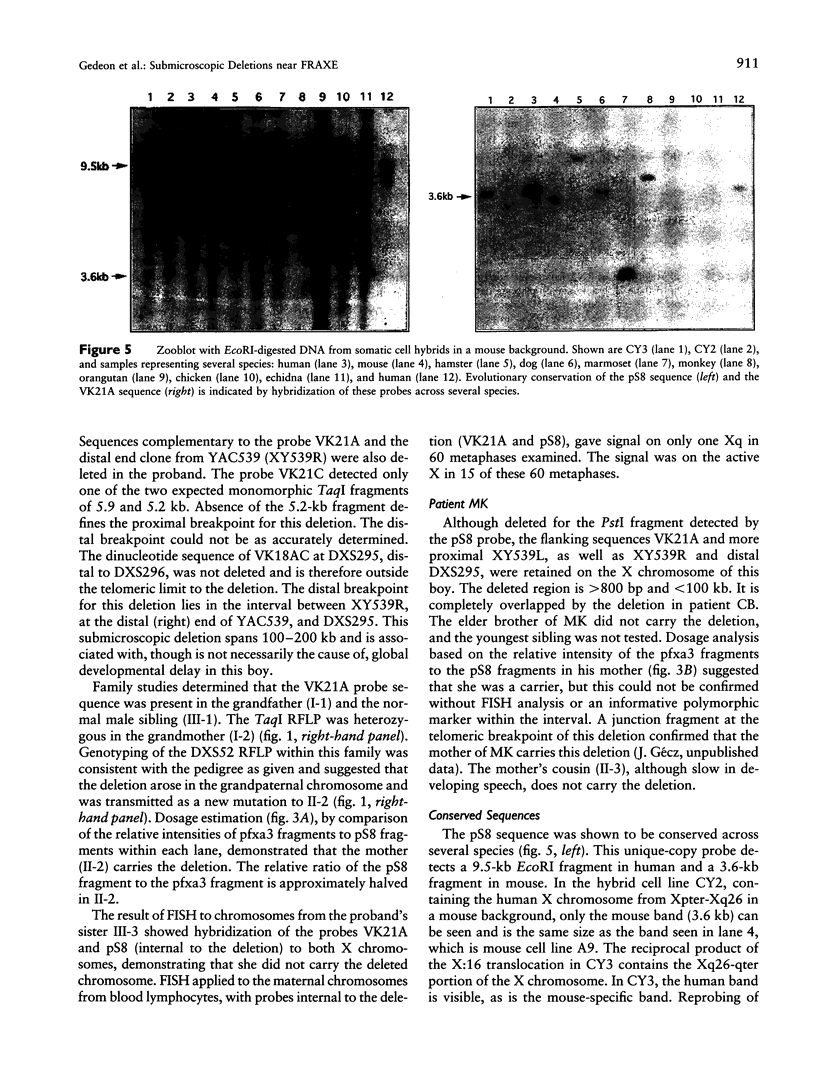
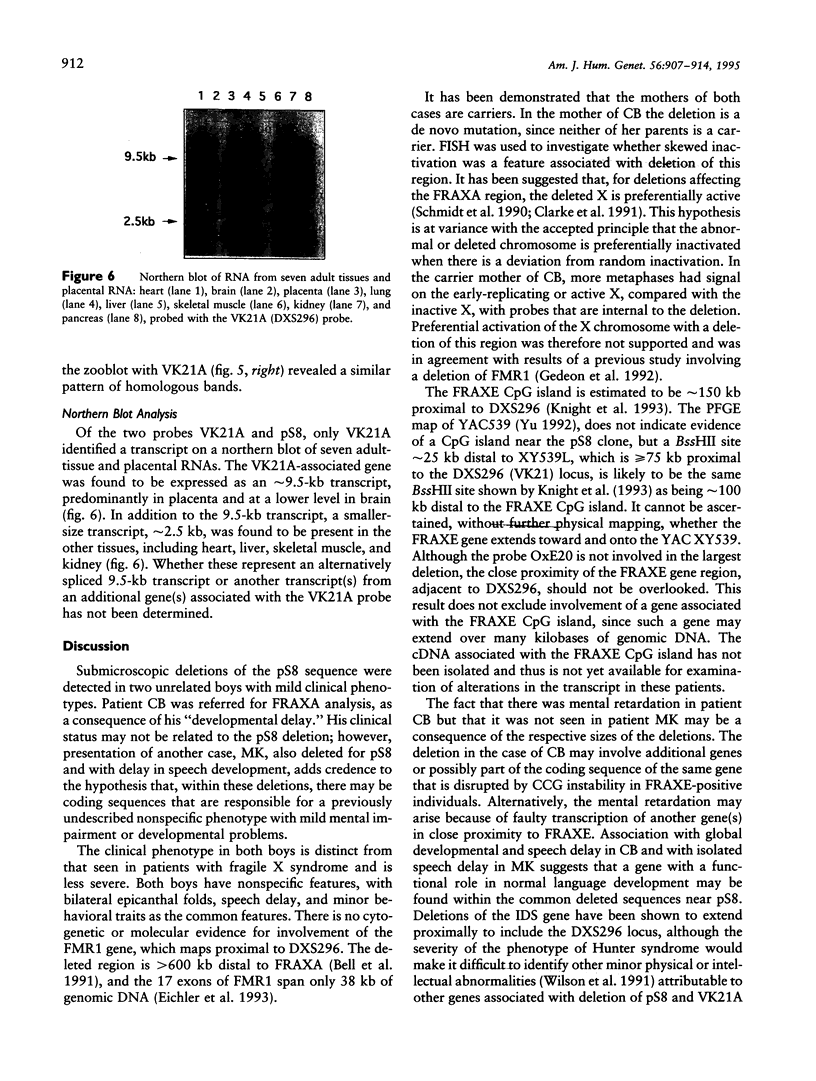
Two unrelated boys are described with delay in development and submicroscopic deletions in Xq28, near FRAXE. Molecular diagnosis to exclude the fragile X (FRAXA) syndrome used the direct probe pfxa3, together with a control probe pS8 (DXS296), against PstI restriction digests of DNA. Deletions were detected initially by the control probe pS8, which is an anonymous fragment subcloned from YAC 539, within 1 Mb distal to FRAXA. Further molecular analyses determined that the maximum size of the deletion is < 100 kb in one boy (MK) and is wholly overlapped by the deletion of up to approximately 200 kb in the other (CB). These deletions lie between the sequences detected by the probe VK21C (DXS296) and a dinucleotide repeat VK18AC (DXS295). The patient MK had only speech delay with otherwise normal development, while patient CB had global developmental delay that included speech delay. Detection of overlapping deletions in these two cases led to speculation that coding sequences of a gene(s) important in language development may be affected. Hybridization of the pS8 and VK21A probes to zooblots revealed cross-species homology. This conservation during evolution suggested that this region contains sequences with functional significance in normal development. The VK21A probe detected a 9.5-kb transcript in placenta and brain and a smaller, 2.5-kb, transcript in other tissues analyzed.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Albright S. G., Lachiewicz A. M., Tarleton J. C., Rao K. W., Schwartz C. E., Richie R., Tennison M. B., Aylsworth A. S. Fragile X phenotype in a patient with a large de novo deletion in Xq27-q28. Am J Med Genet. 1994 Jul 15;51(4):294–297. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320510403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell M. V., Hirst M. C., Nakahori Y., MacKinnon R. N., Roche A., Flint T. J., Jacobs P. A., Tommerup N., Tranebjaerg L., Froster-Iskenius U. Physical mapping across the fragile X: hypermethylation and clinical expression of the fragile X syndrome. Cell. 1991 Feb 22;64(4):861–866. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90514-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choo K. H., Brown R., Webb G., Craig I. W., Filby R. G. Genomic organization of human centromeric alpha satellite DNA: characterization of a chromosome 17 alpha satellite sequence. DNA. 1987 Aug;6(4):297–305. doi: 10.1089/dna.1987.6.297. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke J. T., Greer W. L., Strasberg P. M., Pearce R. D., Skomorowski M. A., Ray P. N. Hunter disease (mucopolysaccharidosis type II) associated with unbalanced inactivation of the X chromosomes in a karyotypically normal girl. Am J Hum Genet. 1991 Aug;49(2):289–297. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Boulle K., Verkerk A. J., Reyniers E., Vits L., Hendrickx J., Van Roy B., Van den Bos F., de Graaff E., Oostra B. A., Willems P. J. A point mutation in the FMR-1 gene associated with fragile X mental retardation. Nat Genet. 1993 Jan;3(1):31–35. doi: 10.1038/ng0193-31. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eichler E. E., Richards S., Gibbs R. A., Nelson D. L. Fine structure of the human FMR1 gene. Hum Mol Genet. 1993 Aug;2(8):1147–1153. doi: 10.1093/hmg/2.8.1147. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gedeon A. K., Baker E., Robinson H., Partington M. W., Gross B., Manca A., Korn B., Poustka A., Yu S., Sutherland G. R. Fragile X syndrome without CCG amplification has an FMR1 deletion. Nat Genet. 1992 Aug;1(5):341–344. doi: 10.1038/ng0892-341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ketterling R. P., Vielhaber E. L., Lind T. J., Thorland E. C., Sommer S. S. The rates and patterns of deletions in the human factor IX gene. Am J Hum Genet. 1994 Feb;54(2):201–213. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knight S. J., Flannery A. V., Hirst M. C., Campbell L., Christodoulou Z., Phelps S. R., Pointon J., Middleton-Price H. R., Barnicoat A., Pembrey M. E. Trinucleotide repeat amplification and hypermethylation of a CpG island in FRAXE mental retardation. Cell. 1993 Jul 16;74(1):127–134. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90300-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meijer H., de Graaff E., Merckx D. M., Jongbloed R. J., de Die-Smulders C. E., Engelen J. J., Fryns J. P., Curfs P. M., Oostra B. A. A deletion of 1.6 kb proximal to the CGG repeat of the FMR1 gene causes the clinical phenotype of the fragile X syndrome. Hum Mol Genet. 1994 Apr;3(4):615–620. doi: 10.1093/hmg/3.4.615. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parrish J. E., Oostra B. A., Verkerk A. J., Richards C. S., Reynolds J., Spikes A. S., Shaffer L. G., Nelson D. L. Isolation of a GCC repeat showing expansion in FRAXF, a fragile site distal to FRAXA and FRAXE. Nat Genet. 1994 Nov;8(3):229–235. doi: 10.1038/ng1194-229. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pieretti M., Zhang F. P., Fu Y. H., Warren S. T., Oostra B. A., Caskey C. T., Nelson D. L. Absence of expression of the FMR-1 gene in fragile X syndrome. Cell. 1991 Aug 23;66(4):817–822. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90125-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt M., Certoma A., Du Sart D., Kalitsis P., Leversha M., Fowler K., Sheffield L., Jack I., Danks D. M. Unusual X chromosome inactivation in a mentally retarded girl with an interstitial deletion Xq27: implications for the fragile X syndrome. Hum Genet. 1990 Mar;84(4):347–352. doi: 10.1007/BF00196232. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutherland G. R., Gedeon A., Kornman L., Donnelly A., Byard R. W., Mulley J. C., Kremer E., Lynch M., Pritchard M., Yu S. Prenatal diagnosis of fragile X syndrome by direct detection of the unstable DNA sequence. N Engl J Med. 1991 Dec 12;325(24):1720–1722. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199112123252407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suthers G. K., Hyland V. J., Callen D. F., Oberle I., Rocchi M., Thomas N. S., Morris C. P., Schwartz C. E., Schmidt M., Ropers H. H. Physical mapping of new DNA probes near the fragile X mutation (FRAXA) by using a panel of cell lines. Am J Hum Genet. 1990 Aug;47(2):187–195. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tarleton J., Richie R., Schwartz C., Rao K., Aylsworth A. S., Lachiewicz A. An extensive de novo deletion removing FMR1 in a patient with mental retardation and the fragile X syndrome phenotype. Hum Mol Genet. 1993 Nov;2(11):1973–1974. doi: 10.1093/hmg/2.11.1973. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trottier Y., Imbert G., Poustka A., Fryns J. P., Mandel J. L. Male with typical fragile X phenotype is deleted for part of the FMR1 gene and for about 100 kb of upstream region. Am J Med Genet. 1994 Jul 15;51(4):454–457. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320510431. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verkerk A. J., Pieretti M., Sutcliffe J. S., Fu Y. H., Kuhl D. P., Pizzuti A., Reiner O., Richards S., Victoria M. F., Zhang F. P. Identification of a gene (FMR-1) containing a CGG repeat coincident with a breakpoint cluster region exhibiting length variation in fragile X syndrome. Cell. 1991 May 31;65(5):905–914. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90397-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson P. J., Suthers G. K., Callen D. F., Baker E., Nelson P. V., Cooper A., Wraith J. E., Sutherland G. R., Morris C. P., Hopwood J. J. Frequent deletions at Xq28 indicate genetic heterogeneity in Hunter syndrome. Hum Genet. 1991 Mar;86(5):505–508. doi: 10.1007/BF00194643. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wöhrle D., Kotzot D., Hirst M. C., Manca A., Korn B., Schmidt A., Barbi G., Rott H. D., Poustka A., Davies K. E. A microdeletion of less than 250 kb, including the proximal part of the FMR-I gene and the fragile-X site, in a male with the clinical phenotype of fragile-X syndrome. Am J Hum Genet. 1992 Aug;51(2):299–306. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu S., Pritchard M., Kremer E., Lynch M., Nancarrow J., Baker E., Holman K., Mulley J. C., Warren S. T., Schlessinger D. Fragile X genotype characterized by an unstable region of DNA. Science. 1991 May 24;252(5009):1179–1181. doi: 10.1126/science.252.5009.1179. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]