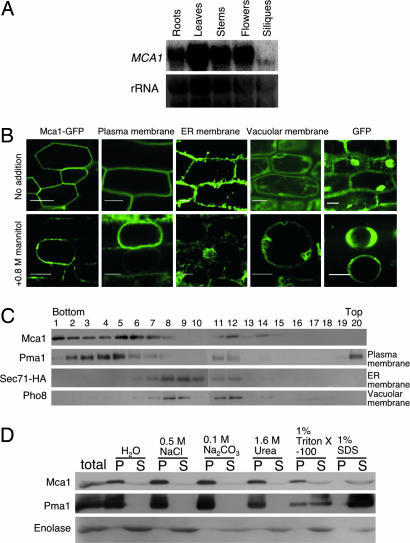
Fig. 2.
Expression of MCA1. (A) Northern blotting of the MCA1 transcripts. Total RNA was isolated from roots, leaves, stems, flowers, and siliques of mature Arabidopsis plants and subjected to Northern blotting. rRNA was used for internal controls for the amount of RNA loaded. (B) GFP fluorescence images suggesting the localization of Mca1-GFP in the plasma membrane of root cells. The upper row represents intact roots and the bottom row those treated with 0.8 M mannitol for at least 10 min. Note that mannitol induced plasmolysis. The sample and membrane marker proteins used are as follows: Mca1-GFP, a GFP fusion to the C terminus of the full length Mca1 protein; Plasma membrane, a GFP fusion to the plasma membrane channel protein PIP2A expressed in line Q8 (27); ER membrane, a GFP fusion to an endoplasmic reticulum membrane protein expressed in line Q4 (27); Vacuolar membrane, a GFP fusion to the vacuolar membrane channel protein delta-TIP expressed in line Q5 (27); and cytoplasmic GFP. (Scale bars, 20 μm.) (C) Membrane fractionation by sucrose density gradient centrifugation and localization of Mca1 expressed in yeast. Pma1, plasma membrane H+-ATPase; Sec71-HA, an endoplasmic reticulum membrane protein tagged with hemagglutinin antigen (HA); Pho8, a vacuolar membrane protein. (D) Mca1 is an integral membrane protein in yeast. Note that Mca1 is not solubilized with NaCl, Na2CO3, and urea, all of which are known to solubilize peripheral membrane proteins. P, pellet after centrifugation at 100,000 × g for 1 h, containing membranes; S, supernatant.