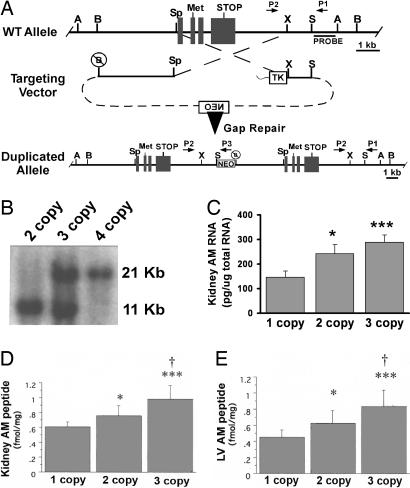
Fig. 1.
Generation of AM gene-titration mice. (A) Targeting strategy used to generate mice with a duplication of the AM gene on chromosome 7. The targeting vector consisted of regions of homology that flank the entire AM gene so that all sequences between the endogenous 5′ BamH1 site and 3′ Sac site were duplicated in the second copy. Primers to identify ES cells are labeled P1, P2, and P3. (B) Southern blot of correctly targeted ES cells by using genomic DNA digested with BamH1 and the probe sequence depicted in A. The wild-type allele is 11 kb, and the targeted allele is 21 kb. (C) Levels of AM RNA in kidney of one-, two-, and three-copy mice measured by quantitative RT-PCR. (D) Levels of AM peptide in kidney of one-, two-, and three-copy mice measured by RIA. (E) Levels of AM peptide in left ventricle (LV) of one-, two-, and three-copy mice measured by RIA. A, AvrII; B, BamH1; Sp, Spe; X, Xba; S, SacI. ∗, P < 0.05 vs. one-copy; ∗∗∗, P < 0.001 vs. one-copy; †, P < 0.05 vs. two-copy. n > 5 for each genotype in C–E. Error bars represent SEMs.