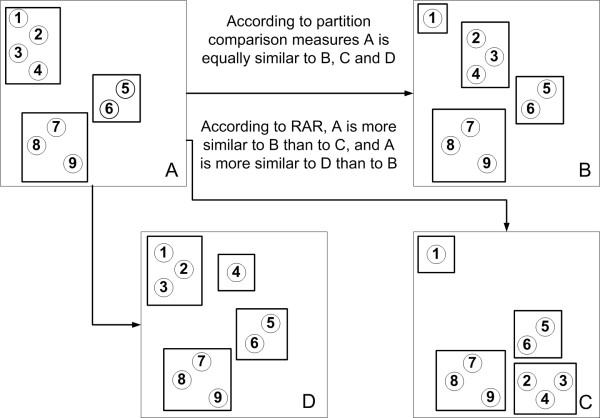
Figure 1.
Small clusterings example of RAR's unique properties. Clustering A divides 9 points (numbered circles) in three clusters identified by rectangles. By splitting the {1, 2, 3, 4} cluster, the clusterings B, C and D were formed. One of the child clusters kept the same location. The second child cluster moved away from the original location. In B and C, the second child cluster has only one entity, while in D it has three. In B and D the two split clusters are nearest neighbours, while in C they are maximally separated. The two dimensional coordinates of the points in the figure were used to compute average distances between clusters and to calculate RAR and other clustering comparison measures. The results are presented in Table 4.