Fig. 5.
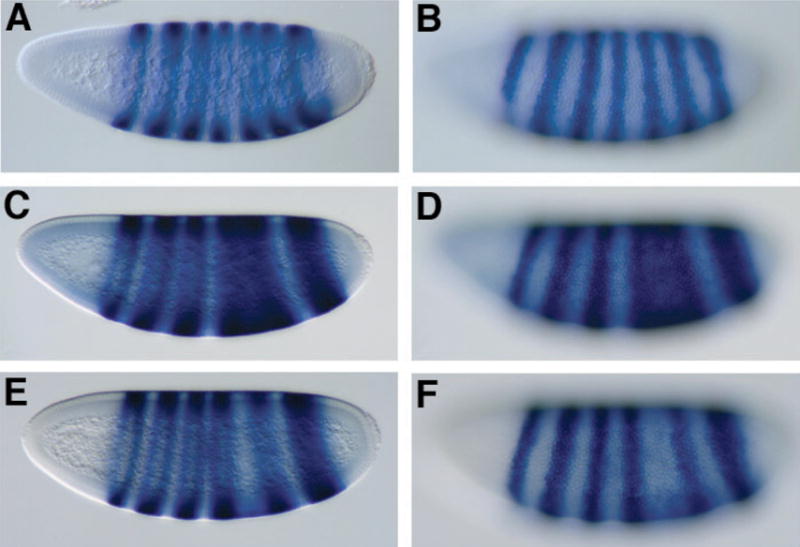
eve expression patterns reveal genetic interaction between rpd3 and knirps in doubly heterozygous embryos. eve expression was analyzed by in situ hybridization of embryos from wild-type strains (A, B) or from crosses of rpd3 and kni heterozygous mutants (C–F). A, B Wild-type eve expression in a mid cycle 14 embryo; C, D eve expression showing fusion of eve stripes 4–6, characteristic of a large percentage of embryos from double heterozygous cross and a smaller fraction of kni heterozygous embryos; this embryo from kni9/+, rpd3def24/+ cross. E, F attenuation of eve stripe 5 embryo characteristic of a large percentage of embryos from double heterozygous cross and a smaller fraction of embryos from kni heterozygotes; this embryo from kni9/+, rpd3def24/+ cross. Identical phenotypes were observed in crosses with kni7G and rpd04556 (Table I). Embryos were fixed and hybridized with antisense eve RNA to visualize expression of the eve gene, and are oriented with dorsal up, anterior pole to the left. A, C, E parasagittal sections; B, D, F surface images of the embryos at left.
