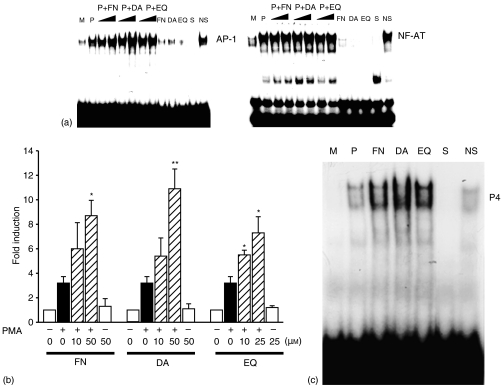
Figure 4.
FN, DA and EQ enhance AP-1 activation induced with PMA. (a) FN, DA and EQ enhance AP-1 DNA binding activity. Nuclear extracts from EL4 cells stimulated by PMA in the presence of FN, DA and EQ were examined for AP-1 and NF-AT DNA binding activity in the EMSA, using radiolabelled oligonucleotides containing a AP-1 site or NF-AT site, respectively. S and NS indicate the presence of an unlabelled, specific oligonucleotide (NF-AT and AP-1) and non-specific oligonucleotide (CRE or NF-κB), respectively. (b) Transfection of EL4 cells with AP-1 minimal promoter construct, followed by stimulation with PMA (1 ng/ml) in the absence or presence of FN, DA and EQ. The results are represented as the induction fold over the value obtained with unstimulated EL4 cells transfected with the promoter construct with given an arbitrary value of 1. The data are representative of three independent experiments. (c) Nuclear extracts from EL4 cells stimulated by PMA in the presence of FN (50 µm), DA (50 µm) and EQ (25 µm) were examined for P4 region DNA binding activity in the EMSA, using P4 radiolabelled oligonucleotides containing an AP-1 site. S and NS indicate the presence of an unlabelled, specific oligonucleotide (P4) and non-specific oligonucleotide (mutP4), respectively. *P < 0·005 and **P < 0·0005, compared with the EL4 cells treated with PMA alone.