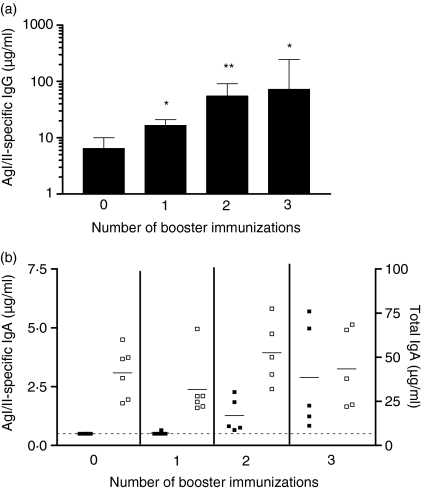
Figure 4.
Surface antigen AgI/II-specific immunoglobulin (IgG) in serum(a)and AgI/II-specific and total IgA in saliva(b)following one, two or three intranasal (i.n.) booster immunizations. Groups (n = 5–6) were primed i.n. with a genetically coupled protein composed of the saliva-binding region (SBR) of the Streptococcus mutans surface antigen AgI/II and the non-toxic A2 and B subunits of cholera toxin (CT) (SBR-CTA2/B) on days 0, 10 and 20 and rested for 6 months before boosting i.n. with SBR-CTA2/B 1, 2 or 3 times at 10-day intervals. Animals not boosted (zero boost) served as a control. Samples were collected 7 days after the final booster immunization or at the 7-month time-point for the group not boosted. Serum antibody data are represented as the geometric mean and standard deviation. *P < 0·05 and **P < 0·01 compared with animals not boosted (a). Salivary antibody responses are shown for individual animals (b; closed symbols, specific IgA; open symbols, total IgA). The line denotes the lowest detectable limit of 0·5 µg/ml.