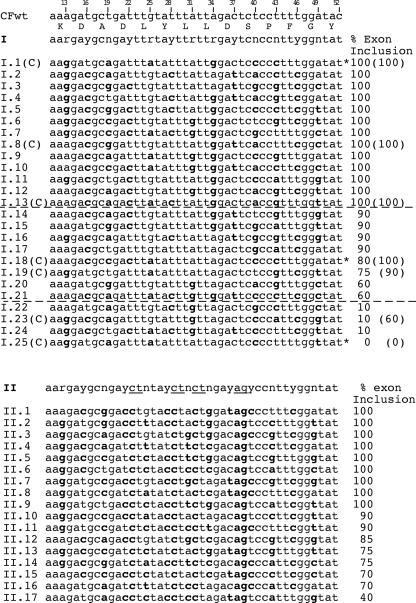
Figure 2.
Effect of CFTR exon 12 random multiple synonymous substitutions on the splicing efficiency. The two 13-degenerated codons oligonucleotides I and II were cloned in the CFTR exon 12 to create random changes at synonymous sites between the exonic positions 13 and 52. Resulting hybrid minigenes (I.1 to I.25 and II.1 to II.17) were then isolated and individually analyzed for splicing efficiency. The position of the mutations relative to the wild-type (CFWT) exon is shown at the top and synonymous mutations are in bold in comparison to human sequence. Number on the right of each sequence indicates the percentage of exon inclusion as determined by minigene splicing assay and is the mean of three independent experiments done in duplicate. In some clones derived from degenerated oligonucleotide I (indicated with a additional (C)) we changed the T52 to the wild-type C52 and the resulting percentage of exon inclusion is indicated in parenthesis on the right. The clones with the asterisks I.1, I.18 and I.25 were selected for subsequent experiments shown in Figure 4. Compared with WT sequence the I mutants showed a mean of 7.6 synonymous substitutions, the II mutants 15.6.