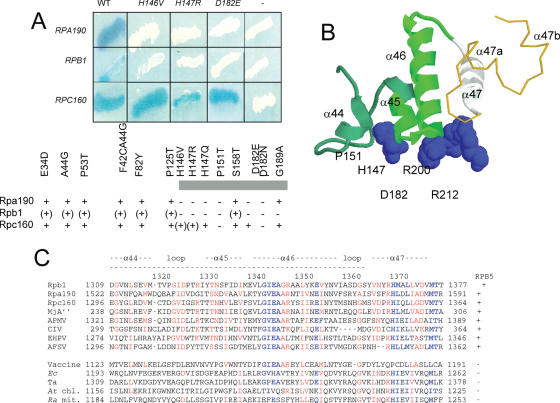
Figure 4.
Binding of Rpb5 to the Rpb1-α44/47-fold (A) Two-hybrid interactions between Rpb5 and Rpa190, Rpb1 and Rpc160. Wild-type and mutant forms of Rpb5 fused to Gal4BD in plasmid pAS2Δ were tested against plasmids pACT2-RPA190(1615), pACT2-RPB1(1545) and pACT2-RPC160(1594) listed in table 1 and containing the partner regions of Rpa190, Rpb1 and Rpc160 fused to the Gal4AD domain of pACT2. β-Galactosidase was tested in an overlay assay (29), as shown for the RPB5, rpb5-H146V, rpb5-H147R and rpb5-D182E constructs and as summarized below for the other mutants. +, (+) and − denote positive, reduced and negative responses in the β-galactosidase plate assay, respectively. (B) Spatial organization of H147, P151, D182, R200 and R212 relatively to the Rpb1α44/47-fold in the elongating RNA polymerase II. H147, P151, D182, R200 and R212 positions of Rpb5 are space-filled. The Rpb1-α44/46-fold (positions 1309–1362, corresponding to the minimal two-hybrid domain of Figure 4A is shown in green ribbons. The Rpb1-α47 helix (positions 1363–1377), not comprised in the minimal two-hybrid domain but binding Rpb5, notably through position R212) is shown in white ribbons. A gold thin line corresponding to Switch 1 backbone (positions 1378–1403). (C). Sequence conservation of the Rpb1-α44/47 domains. Highly conserved domain are blue. Species symbols: Sc (S.cerevisiae); Mj (M.jannaschii), Ec (Escherichia coli); Ta (T.aquaticus); At (A.thaliana, chloroplastic), Ra (R.americana, mitochondrial). Viral species: Acanthamoeba Polyphaga Mimivirus (APMV); Chilo Iridescent Virus (CIV); Emiliana Huxleyi PhycoDNA Virus (EHPV); African Swine Fever Virus (AFSV) and Vaccine.