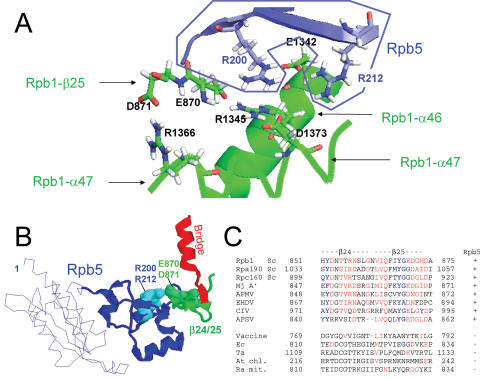
Figure 5.
Dual binding of Rpb5 to Rpb1 (A) View of the salt bridge system involving R200 and R212 (Rpb5) and six Rpb1 amino acids: E870, D871 (Rpb1-β25), E1342 and R1345 (Rpb1-α46), R1366 and D1373 (Rpb1-α47). Drawing based on the PDB crystallographic coordinates 1I6H (41), with Hydrogen atoms recalculated by the PDB-viewer programme. The Rpb5 domain is in blue, and the two Rpb1 parts in green. (B) Spatial organization of Rpb5, the Rpb1-β24/25-fold and the Bridge helix (Rpb1-α25), using the same orientation as in Figure 1. Rpb5 is shown in blue, with the eukaryotic backbone domain shown as a thin line. R200 and R212 are space-filled. Rpb1-β24/25 and Rpb1-α25 are shown in green and red, respectively. (C) Conservation of the Rpb1-β24/25 sequence. Species symbols as in Figure 4. Conserved amino acids are in red.