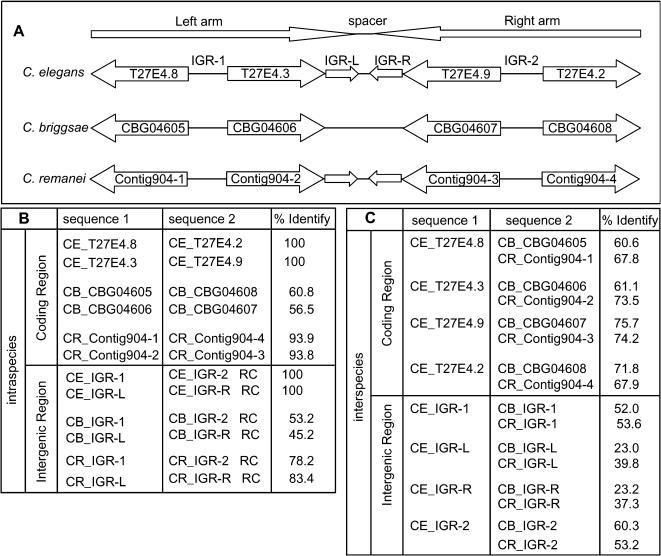
Figure 2.
An example of convergently oriented inverted repeat. A. Schematic representation of the inverted repeat structure of C. elegans T27E4.3 - T27E4.9 genomic region as well as C. briggsae and C. remanei orthologous genomic region. In C. elegans, the region of T27E4.8, IGR-1, T27E4.3 and IGR-L is a perfect mirror image of the region of T27E4.2, IGR-2, T27E4.9 and IGR-R. In C. remanei, Contig904-snap.9.final (Contig904-1), Contig904-eannot.018.final.final (Contig904-2), Contig904.eannot.1017.final.final (Contig904-3) and Contig904.snap.4.final (Contig904-4) have similar inverted repeat structure. In C. briggsae, CBG04605, CBG04606, CBG04607 and CBG04608 are arranged in the same orientation but don't have inverted repeat structure. B. Sequence comparison was carried out between sequence 1 and sequence 2 for each row. Sequence identity within each species (intraspecies) in a global alignment (Needleman-Wunsch) is shown in the last column of the table. C. Sequence identity between species (interspecies) is shown in the last column of the table. Sequence identity within a species is much higher than the sequence identity between species for C. elegans and C. remanei. CE: C. elegans; CB: C. briggsae; CR: C. remanei; IGR: intergenic region.