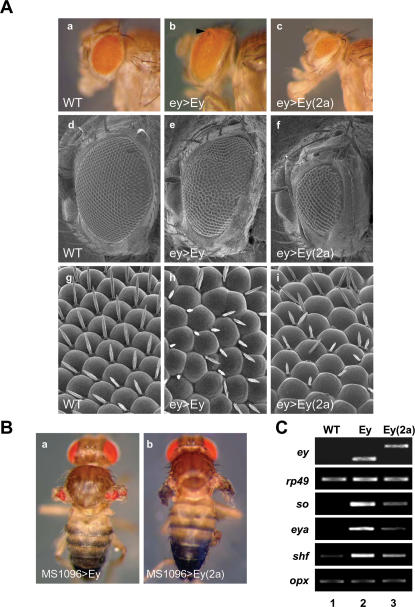
Figure 4.
Over-expression of Ey(2a) and Ey isoforms leads to different phenotypes. (A) Representative eye phenotypes obtained after expression of Ey (panel b) or Ey(2a) (panel c) isoforms under the control of ey-Gal4, compared to wild-type flies (panel a). Ey isoform expression induces strong disorganization of the ommatidia lattice (compare panels e and d). Ommatidia appear of variable size with possible fusion between them, as observed in (panel h). ey>Ey flies often display local overgrowth in the eyes (arrowhead in panel b). Expression of the Ey(2a) isoform only reduces the size of the eye (panels c and f) with moderate disorganization of the omatidia lattice (panel i). (B) Expression of Ey (panel a) and Ey(2a) (panel b) isoforms under the control of MS1096. (C) Ectopic expression of Ey and Ey(2a) in the wing induces expression of downstream target genes at different levels. RT-PCR analyses were performed to measure the expression of eyeless (panel ey), the ribobosomal Rp49 (panel rp49), Sine oculis (panel so), eyes absent (panel eya), shifted (panel shf) and Optix (panel opx) mRNAs in wing discs from wild type (lane 1) MS1096>Ey (lane 2) and MS1096>Ey(2a) (lane 3) third instar larvae.