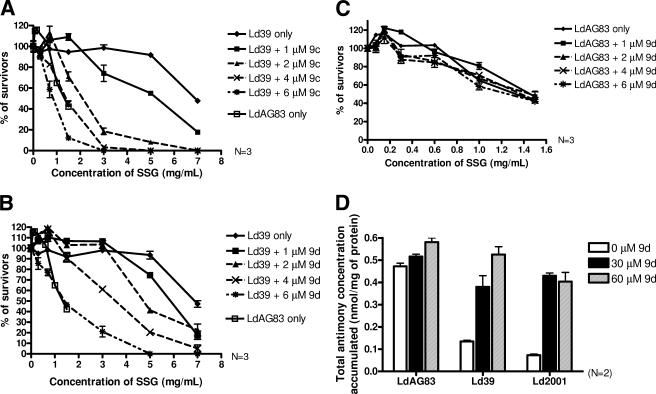
FIG. 6.
Dose-dependent modulating activity of 9c and 9d on the SSG resistance of Ld39. SSG-resistant Ld39 promastigotes were seeded at 105 cells/well in 100 μl and incubated at 27°C for 72 h in the presence of serial dilutions of SSG and 9c (A) or 9d (B). The ⧫, ▪, ▴, ×, and ✠ symbols represent 0, 1, 2, 4, and 6 μM 9c or 9d, respectively. Wild-type LdAG83, without 9c, was included as control (□). SSG-sensitive LdAG83 promastigotes were studied by using the same protocol as described above. (C) The percentage of survivors was quantified by using MTS assay after 72 h of incubation at 27°C. Each datum point was tested in triplicate, and analyses were repeated three times in separate experiments. Note that the concentration of SSG used for Ld39 is different from that of LdAG83. The effect of 9d on the SSG accumulation of LdAG83, Ld39, and Ld2001 was studied in panel D. A 1-ml portion of 4-day-old axenic amastigotes at a cell density of 2 × 108 cells/ml was incubated at 37°C for 3 h with 0.05 mM SSG and various concentrations of 9d (0, 30, or 60 μM). After incubation, the cells were washed with PBS, and the total antimony concentration was determined by ICP-MS. Each concentration of 9d was tested in triplicate, and analyses were repeated twice in separate experiments. The total antimony concentration is presented as nmol per mg of protein (mean ± standard error mean, n = 2). The white bar, black bar, and striped bar represent 0, 30, and 60 μM 9d, respectively.