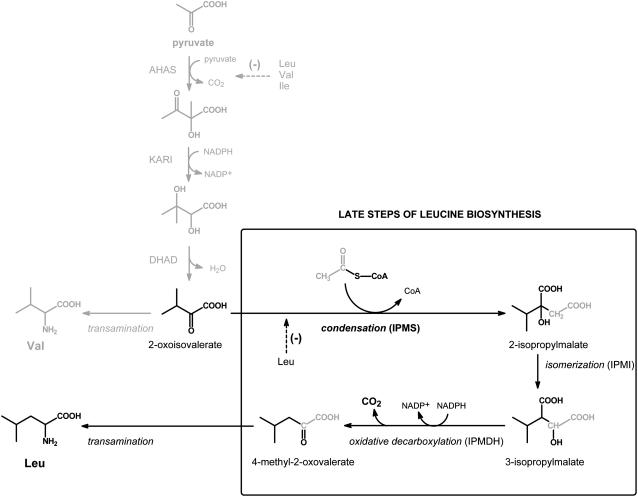
Figure 1.
The biosynthesis of Leu and Val from pyruvate. The action of acetohydroxyacid synthase (AHAS), ketoacid reductoismerase (KARI), and dihydroxyacid dehydratase (DHAD) yields 2-oxoisovalerate that is either transaminated to Val or subjected to additional reactions specific for Leu biosynthesis. The dedicated step in Leu biosynthesis is the aldol-type condensation between 2-oxoisovalerate and acetyl-CoA that results in formation of 2-isopropylmalate. Isomerization and oxidative decarboxylation by isopropylmalate isomerase (IPMI) and isopropylmalate dehydrogenase (IPMDH) yield 4-methyl-2-oxovalerate that is transaminated to Leu. The enzymes that catalyze the reactions from pyruvate to 2-oxoisovalerate are also involved in biosynthesis of Ile, using 4-oxobutyrate (product of Thr dehydratase) as an initial substrate, but for simplicity have not been depicted. AHAS and IPMS are subject to feedback inhibition as shown with dashed lines.